For decades, the biggest barrier to entry for entrepreneurs was technical talent. If you couldn’t write code, you had to find a technical co-founder or pay an agency tens of thousands of dollars. That era is effectively over. The ecosystem has matured to the point where you can launch a startup app with no-code and go from a napkin concept to a real, revenue-generating product without writing a single line of syntax.
In fact, a Non-Developer Launched a Startup App With No-Code, demonstrating how accessible this process has become.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildThis guide is built for non-developers who want practical steps, realistic expectations, and a clean path to launch. You’ll learn how to validate your idea, define an MVP, choose the right no-code stack, build confidently, and launch with traction.
We will also look at how the landscape is shifting in 2026, specifically how AI-led no-code builders are simplifying the process even further by handling not just the UI, but the future of building software.
What No-Code Really Means (And What It Doesn’t)
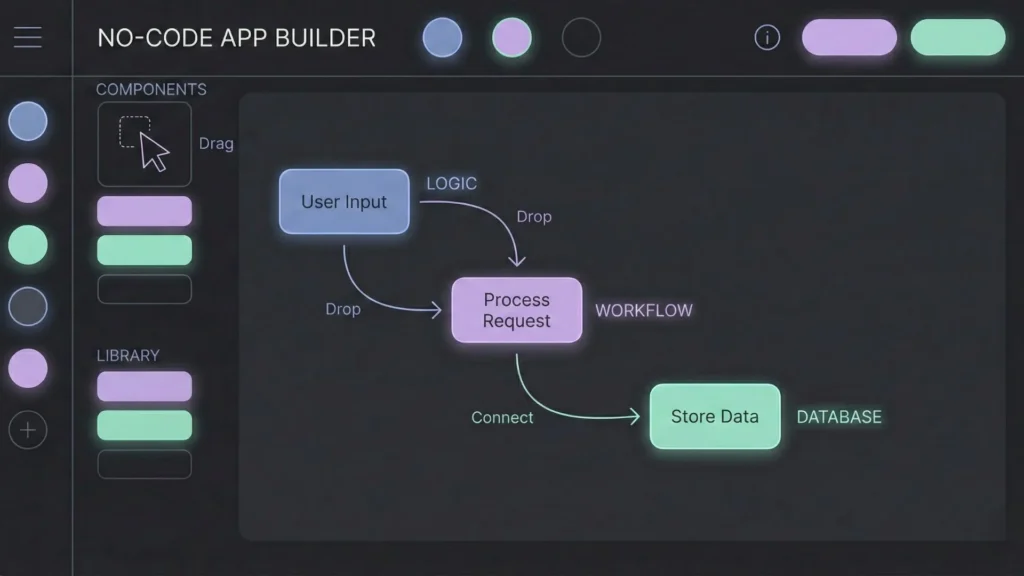
No-code means you build software using visual interfaces instead of writing text-based code. You drag and drop components (buttons, forms, images), connect workflows visually (if user clicks X, do Y), and store data in tables that look suspiciously like spreadsheets.
What no-code is great for:
- Launching no-code MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) in weeks, not months.
- Testing market demand before spending capital on custom engineering.
- Building internal tools, dashboards, marketplaces, booking apps, and SaaS platforms.
- Iterating immediately based on user feedback without waiting for a developer sprint.
What no-code isn’t magically solving:
- Product Thinking: You still need to understand user flows and logic.
- Data Structure: A bad database structure will break a no-code app just as fast as a coded one.
- Business Viability: A beautiful app that solves a fake problem will still fail.
The advantage is simple: You can spend your energy on what to build and why, rather than struggling with the syntax of how.
Step 1: Start With a Real Problem, Not a “Cool App Idea”

As a non-technical founder, your superpower is likely your industry expertise or your empathy for a specific customer. Lean into that. Instead of saying, “I want to build a marketplace for dog walkers,” start with, “Dog owners in cities struggle to find trustworthy walkers on short notice.”
How to write a strong problem statement
Use this formula to keep yourself honest:
- Who: The specific user segment.
- Pain: What frustrates them today.
- Impact: Why it matters (time lost, money lost, emotional stress).
- Current Workaround: What they are doing right now to solve it.
Example:
“Local artisans (Who) struggle to sell consistently because they can’t reach buyers nearby (Pain). This costs them 40% of their potential monthly revenue (Impact). Currently, they depend on Instagram DMs, which are messy, unorganized, and lack payment protection (Workaround).”
Validate the problem with real conversations
Before you touch any builder, validate your startup idea by talking to 10 to 20 people in your target audience. Do not pitch them your idea. Ask about their life.
Good questions to ask:
- “Walk me through how you solve this specific problem today.”
- “What is the most annoying part of that process?”
- “How much time or money does this problem cost you?”
- “Have you tried other tools? Why did you stop using them?”
If people cannot describe the pain clearly, or if they aren’t actively trying to solve it, your “problem” might not be strong enough to build a business around.
Step 2: Validate Fast With an MVP Mindset
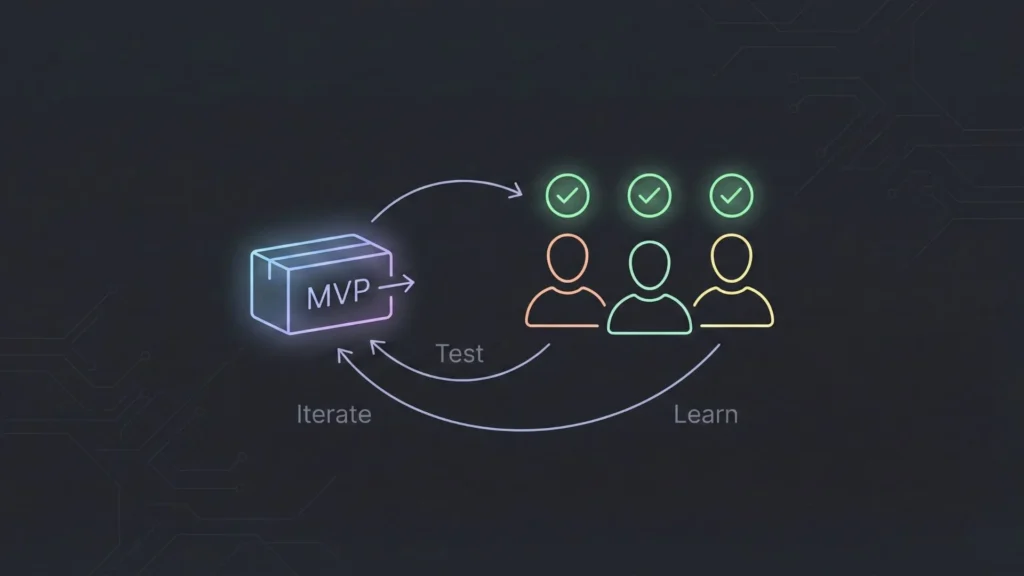
An MVP is not a smaller, uglier version of your dream app. It is the simplest version of the product that proves valid demand.
Your goal is not to impress people with features. Your goal is to answer three questions:
- Will users perform the core action?
- Will they return a second time?
- Will at least some users pay (or commit time)?
How to decide what goes into the MVP
Pick one core job the app does. Then, categorize your feature ideas using a guide for building your MVP:
- Must-Have (MVP): If you remove this, the app doesn’t solve the problem.
- Nice-to-Have (Later): Useful, but the user can live without it for a month.
- Fantasy Features (Ignore): AI personalization, gamification, dark mode, etc.
A strong MVP usually consists of:
- Simple onboarding and secure login.
- One core workflow (e.g., booking a slot, posting an item, generating a report).
- Basic data storage.
- Simple notifications (email or push).
- A single loop (invite a friend, share a result).
If your MVP plan requires 3 months to build, it is not minimal. Aim for 4 to 6 weeks.
Step 3: Pick the Right No-Code Stack
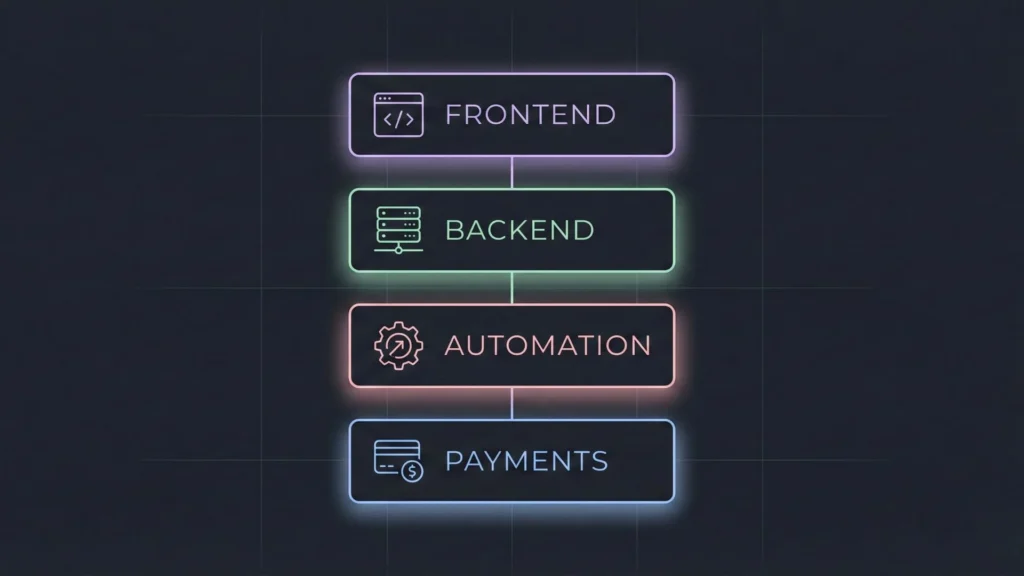
“No-code” is not a single tool; it is a stack of tools working together. In 2026, the market is segmented by what you are trying to build. You need to choose the best stack for building SaaS without code based on your specific needs.
Web Apps
Best when your product is complex, data-heavy, or used primarily on desktop/browsers.
- Use cases: Dashboards, SaaS tools, marketplaces, CRMs, admin panels.
- Why: If you need to build a web app without coding, web-first builders offer more flexibility with logic and larger screen real estate.
Mobile Apps
Best when the user experience depends on being “on the go.”
- Use cases: Fitness trackers, field inspection tools, social networking, on-demand services.
- Why: You need to build a mobile app without coding if you require access to native device features like the camera, GPS, biometrics, and push notifications.
Automation and Integrations
Most apps need to talk to the outside world. You will likely need an automation layer to connect your app to:
- Email providers (transactional emails).
- Payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal).
- External CRMs or spreadsheets.
Databases and Backends
Many visual builders come with a built-in database. For an MVP, this is usually sufficient. However, if you expect high data volume or complex security rules, you might want to look at “backend-as-a-service” tools. This separates your data from your front end, allowing you to scale more easily later.
Step 4: Design UX That People Actually Use
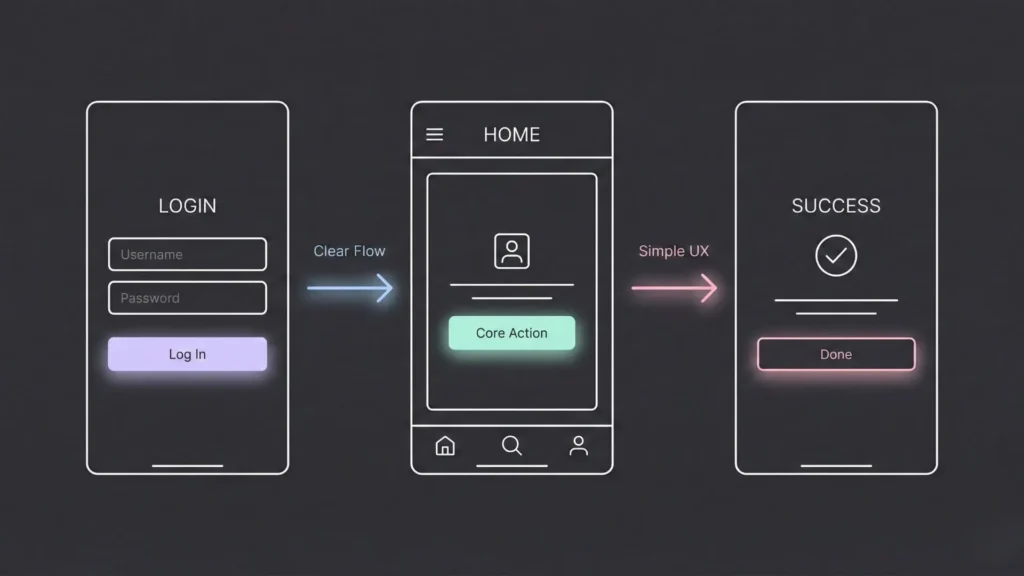
In the no-code world, design isn’t about decoration. It is about conversion. If a user gets confused on screen two, they bounce. They don’t care that you built it without code; they only care if it works.
Wireframe before you build
Never start building directly in the tool. It’s too easy to get distracted by colors and fonts. Start with low-fidelity wireframes you can even learn how to transform sketches into AI-powered apps to speed this up.
Map the Top 3 User Flows:
- First-time Onboarding: How does a stranger become a user?
- Core Action: What is the main thing they came to do?
- Return Usage: What brings them back?
When in doubt, make your product boringly clear. Standard buttons, standard navigation bars, and clear labels beat “innovative” design every time.
Step 5: Build the Database First (Yes, First)
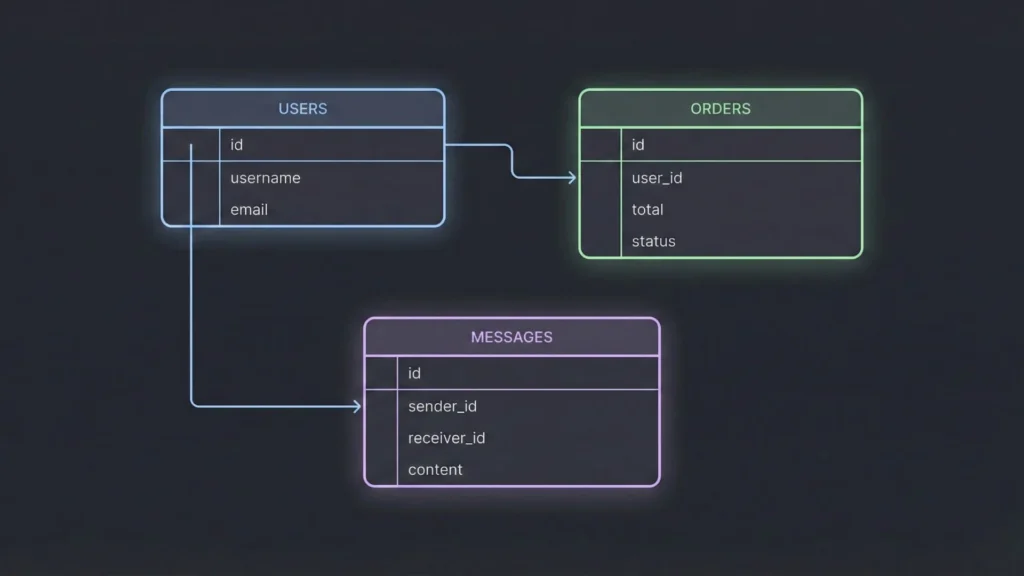
This is the step most non-technical founders skip, and it is the reason most projects fail to scale. A messy database creates a messy product.
Before you build a single screen, you must define your data model.
Identify your core tables
Think of these as the “nouns” in your app.
- Users
- Listings
- Orders
- Messages
- Reviews
Define the relationships
You need to map how these tables talk to each other.
- One-to-Many: A User can have many Orders. An Order belongs to one User.
- Many-to-Many: A Student can take many Courses, and a Course can have many Students.
Basic rules for good no-code data structure
- Naming Conventions: Keep table and field names simple, consistent, and lowercase.
- Don’t Duplicate Data: Don’t type the user’s address in the “Orders” table if it already lives in the “Users” table. Link to it instead.
- Privacy: Set access rules early. A user should only see their private data, not everyone else’s.
Step 6: Build Features With Visual Logic
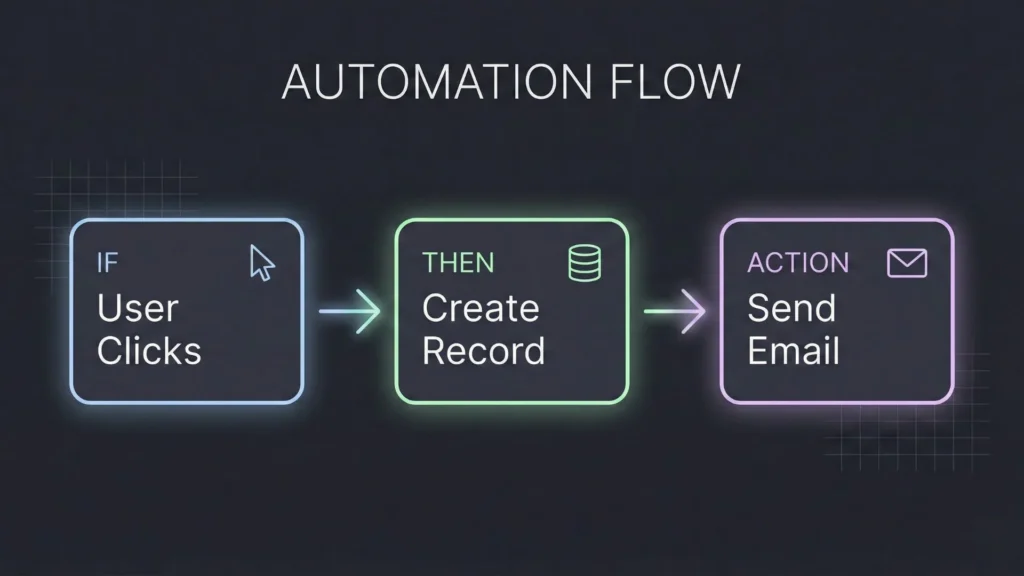
No-code logic is essentially “If This, Then That.” To build complex features, you must break them down into micro-actions.
For example, the sentence “User books an appointment” is actually a chain of five logic steps. When you are automating workflows without writing code, it looks like this:
- User clicks a time slot.
- App checks the database: Is this slot still free?
- If yes, App creates a new row in the
Bookingstable. - App triggers an email to the User (Confirmation).
- App triggers an email to the Admin (Notification).
When you break features down this way, no-code becomes straightforward. Focus on clarity over complexity.
Step 7: Add Payments, Email, Analytics, and Growth Basics
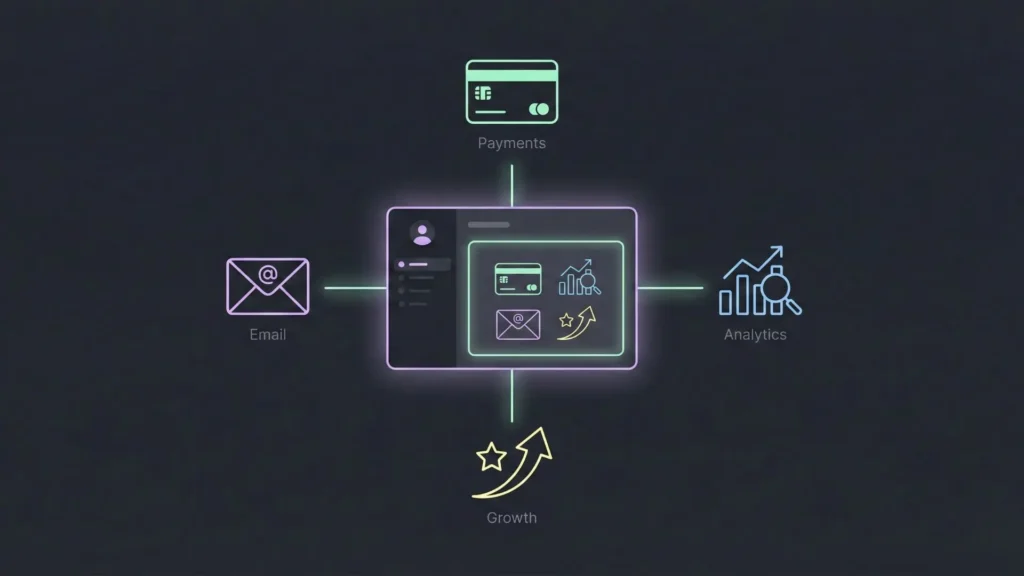
Once the core logic is done, you need to layer on the “business” infrastructure.
- Payments: Keep it simple. Start with a standard subscription model or a simple transaction fee. Handling payment gateway integration is much easier now with plug-and-play components.
- Email: You need at least three emails: Welcome (on signup), Verification (security), and Transactional (receipts/alerts).
- Analytics: You don’t need big data yet. You just need to track Signups, Activation (did they do the core thing?), and Retention (did they come back?).
- Growth Hooks: Build in at least one mechanism that turns users into marketers, such as a referral loop.
Step 8: Test Like a Founder, Not Like a Developer

Testing is not just about finding bugs; it’s about establishing confidence.
Test the “Edge Cases”
Happy paths (where everything goes right) are easy. You need to test the messy paths:
- What happens if I enter a wrong email format?
- What happens if I try to book a slot that was just taken?
- What happens if I click the “Pay” button twice?
- What happens if my internet connection is slow?
Run a small Beta
Get 20 to 50 users into the app. Do not just ask “Do you like it?” Watch their behavior.
- Where do they hesitate?
- What is the first thing they click?
- Where do they drop off?
Fix the confusion points before you launch to the world.
Step 9: Launch Strategy That Doesn’t Feel “Salesy”
A strong launch is quiet, focused, and repeatable. Avoid the “Grand Opening” mentality.
Pre-launch Checklist
- A landing page with clear positioning (solving the problem from Step 1).
- An email waitlist to capture interest.
- A short demo video or high-quality screenshots.
- One clear Call to Action (CTA): “Join,” “Request Access,” or “Start Free.”
The Soft Launch
Launch to your waitlist first, then to niche communities. You need to learn how AI is revolutionizing startup product launches to leverage modern tools for feedback, not just vanity metrics.
Marketing channels that work for no-code startups
- SEO Content: Write problem-based guides. Implementing SEO for AI-built SaaS products is crucial for long-term organic growth.
- Short-form Social: Show the “behind the scenes” of building the app.
- Partnerships: Find creators who speak to your audience and ask them to test it.
- Product Hunt: Save this for when your product is polished and you have a small base of users to support the launch.
Step 10: Scale Without Rebuilding Everything

A common myth is that “no-code doesn’t scale.” In 2026, this is largely false. Scaling is mostly about performance and process.
Improve performance without panic:
- Optimize your database queries (don’t load 10,000 items at once).
- Reduce heavy workflows that run on the client side.
- Ensure you have a scalable SaaS architecture in place from the start.
Improve process as you grow:
- Move from “random fixes” to scheduled weekly releases.
- Maintain a simple roadmap so users know what’s coming.
- Build an internal admin dashboard so you aren’t editing the database manually.
Where AI No-Code Fits (And Why It’s Different)
Traditional no-code platforms are powerful, but they still require you to be a “visual developer.” You have to understand logic, database relationships, and API integrations. For a solo founder, managing the UI builder, the backend, the automations, the hosting, and the QA can become a full-time job.
This is where AI-first builders are shifting the workflow. Instead of manually stitching every piece together, you can now build an app by describing it, and the system architects the foundation for you.
A practical example: Imagine.bo (AI No-Code App Builder)

If you want an educational, founder-friendly way to think about modern AI no-code, Imagine.bo is a prime example of where the category is moving.
At a high level, Imagine.bo helps founders turn a product idea into a revenue-ready app or website by letting them describe requirements in plain English. The system handles the end-to-end build, including architecture, workflows, backend logic, integrations, QA, and launch.
What makes this approach useful especially for non-developers is that it reduces the “tool juggling” fatigue. Instead of paying for and connecting five different subscriptions, you start from your vision and iterate through guided steps.
Key capabilities for founders:
- AI Reasoning: It maps your business goals directly into features and user flows, saving you from “blank canvas syndrome.”
- Production-Grade Standards: It automatically sets up clean, scalable, and secure architecture.
- Cloud Deployment: It handles deployment to robust environments like AWS, GCP, or Vercel seamlessly.
- Security Posture: Designed to be GDPR and SOC2-ready from day one.
- Performance: Built to support high-throughput use cases, ensuring your app doesn’t slow down as you grow.
- Growth Ready: Built-in analytics and SEO/mobile responsiveness are standard.
For a non-technical founder, tools like this significantly reduce the gap between “prototype” and “launchable product,” allowing you to focus on the human side of business: validation, positioning, and customer relationships.
Common No-Code Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
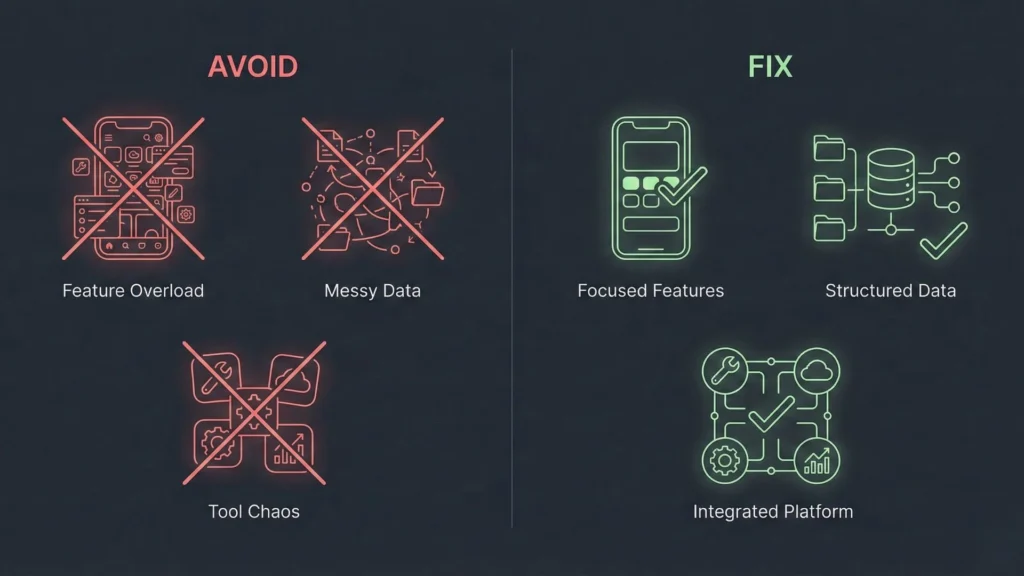
Mistake 1: Building too much before validation.
- Fix: Build the MVP first. Always. If it hurts to cut a feature, cut it anyway.
Mistake 2: Choosing tools based on hype.
- Fix: Choose tools based on your product’s real requirements (e.g., do you actually need a native mobile app, or is a web app fine?).
Mistake 3: Treating data and permissions as an afterthought.
- Fix: Define your database structure and user roles (Admin vs. User) before you design the UI.
Mistake 4: Over-automating everything.
- Fix: Automate only what repeats often. Do things manually first to understand the process.
Mistake 5: Ignoring SEO and acquisition until after launch.
- Fix: Start creating content and building your waitlist the day you start building the app.
For a deeper dive on pitfalls, read about the common mistakes in no-code SaaS development.
Conclusion
No-code has fundamentally changed the founder game. The barrier to entry is no longer technical skill; it is execution and resilience.
If you can clearly define a problem, validate that people care about it, and think logically about how a user moves through a process, you can launch a real app.
Start with a tight MVP. Choose your tools based on requirements, not trends. Build with clean data and simple workflows. Then ship. And if you want to move even faster, look toward AI-first platforms that handle the heavy lifting of architecture for you.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





