No-code and low-code platforms have become essential tools for businesses aiming to accelerate application development without heavy coding. While both reduce the reliance on traditional programming, they serve different needs based on user expertise and project complexity. In 2025, no-code platforms offer faster deployment and accessibility for non-technical users, whereas low-code platforms provide greater customization and flexibility for developers.
Organizations increasingly adopt these platforms to cut costs and improve efficiency across various industries. No-code solutions excel in creating simple, straightforward apps quickly, making them ideal for business users. Low-code platforms, on the other hand, allow developers to build more sophisticated applications with minimal hand-coding.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildChoosing between no-code and low-code depends on the organization’s goals, technical resources, and required application scope. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses select the right approach to meet specific needs and maximize the benefits of digital transformation.
Understanding No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
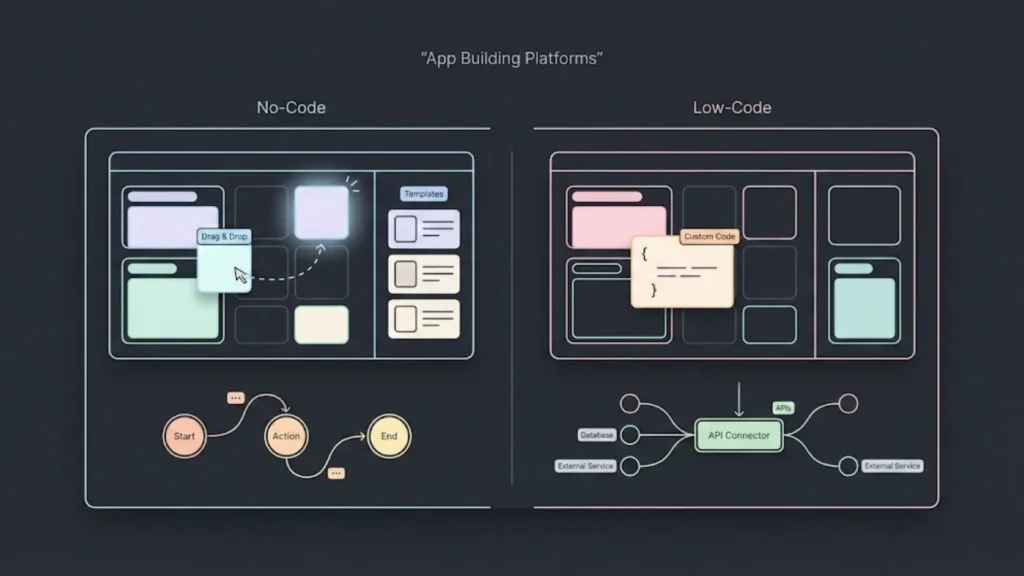
No-code and low-code platforms offer flexible approaches for building applications but differ in technical requirements and customization capabilities. They enable faster development but target users with varying levels of coding experience and project complexity.
Defining No-Code Platforms
No-code platforms allow users to create applications without writing any code. They rely on visual interfaces, drag-and-drop elements, and pre-built templates, making them accessible to non-technical users.
These platforms are suitable for simple-to-moderate projects where customization needs are limited. Users can automate workflows, build web or mobile apps, and integrate standard features with minimal effort.
The main advantage of no-code is speed and ease of use. However, they often have limitations in scalability and customization beyond the provided tools and integrations.
Defining Low-Code Platforms
Low-code platforms require some coding knowledge but greatly reduce the need for manual programming. They provide pre-built components and customizable modules that developers can extend with code as needed.
This approach suits projects demanding more complexity, such as custom integrations, unique business logic, or multi-platform deployment. Low-code supports greater flexibility while still accelerating development compared to traditional coding.
Developers benefit from low-code platforms by saving time on boilerplate tasks and focusing on specialized features. These platforms are well-suited for teams with at least basic programming skills.
Key Differences Between No-Code and Low-Code
| Aspect | No-Code | Low-Code |
|---|---|---|
| User Skill Level | Non-technical users | Basic coding knowledge required |
| Customization | Limited to built-in features | High, with custom code possible |
| Scalability | Suitable for simpler apps | Better support for scaling and complex apps |
| Development Speed | Fastest for small projects | Fast but slightly slower due to coding tasks |
| Use Cases | Business users, rapid prototyping | Professional developers, complex apps |
No-code platforms excel at enabling business users to build straightforward solutions quickly. Low-code platforms strike a balance by allowing technical teams to customize apps while still benefiting from pre-built efficiencies.
No-Code vs Low-Code in 2025: Key Trends
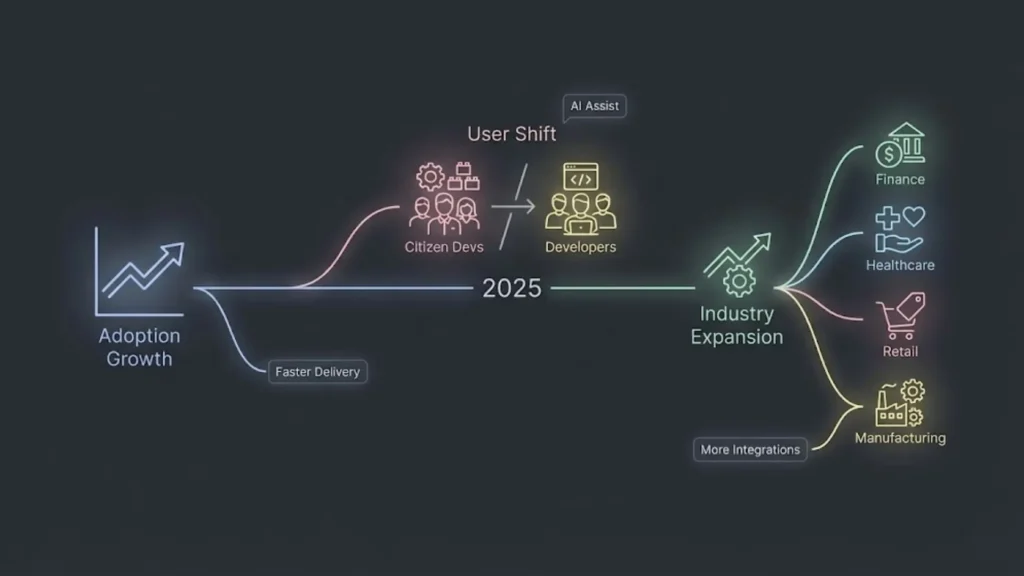
The no-code and low-code landscape in 2025 is marked by rapid adoption, changing user profiles, and expanding industry applications. Distinct shifts in who uses these platforms and how businesses apply them are reshaping software development priorities.
Growth in Platform Adoption
No-code and low-code platforms continue to grow, driven by the need for faster app development and lower costs. In 2025, around 70% of new business applications rely on these tools, reflecting their mainstream acceptance.
Organizations prioritize reducing time-to-market. No-code tools appeal to non-technical users with drag-and-drop simplicity, ideal for quick internal apps or MVPs. Low-code platforms attract IT professionals, providing deeper customization for scalable, enterprise-grade solutions.
This growth is also supported by increased integration capabilities and AI-powered features that simplify automation and enhance user experience. As a result, platform vendors invest heavily in making their offerings more intuitive and flexible.
Shifts in User Demographics
The user base for no-code and low-code platforms is diversifying significantly. Citizen developers—employees without formal coding experience—now lead many app-building initiatives in non-IT departments.
At the same time, professional developers leverage low-code tools to accelerate complex projects, bridging traditional coding and rapid prototyping. This blend increases collaboration across business and technical teams.
Training resources and community support have expanded, enabling more users to contribute. Enterprises encourage this democratization to unlock innovation while maintaining governance through IT oversight.
Evolving Market Segments
In 2025, no-code and low-code platforms serve a broader range of industries than ever before. Small and medium businesses use no-code solutions for simple process automation, while large enterprises deploy low-code for mission-critical applications.
Key sectors adopting these platforms include finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. Each sector benefits from tailored platform features, such as compliance tools, data security, and integration with legacy systems.
The platforms also evolve to address specific needs like customer experience, supply chain optimization, and regulatory reporting. This specialization supports businesses in meeting sector-specific challenges efficiently.
| Market Segment | Typical Platform Use | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Small & Medium Business | Internal tools, automation | Ease of use, low cost |
| Large Enterprises | Scalable apps, integrations | Customization, security, governance |
| Healthcare | Compliance apps | Data security, regulatory support |
| Finance | Workflow automation | Risk management, audit capabilities |
Core Capabilities of No-Code Solutions
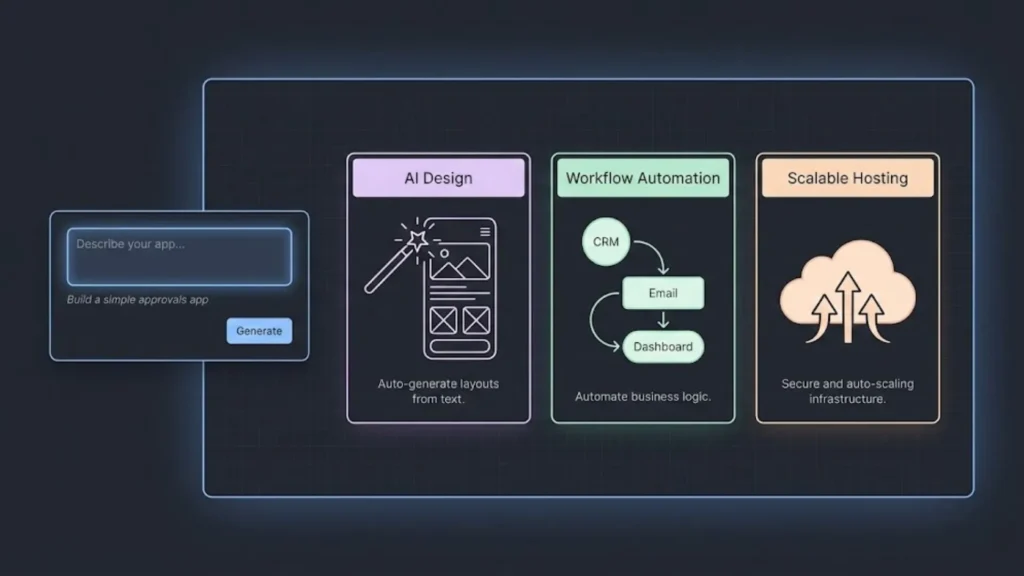
No-code platforms in 2025 emphasize simplifying app creation for users without programming skills. They integrate AI to guide design, automate entire workflows, and support growth through scalable infrastructure. These features reduce technical barriers and accelerate deployment while maintaining professional-grade quality.
AI-Powered Application Design
No-code solutions now frequently incorporate AI-generated blueprints to streamline app development. Platforms like Imagine.bo enable users to start with an AI-suggested structure tailored to their needs, cutting design time drastically.
This approach requires zero-code needed from users, allowing non-technical individuals to build apps quickly. AI assists with layout, component placement, and logic suggestions, enhancing both speed and accuracy.
The result is professional-grade quality applications that meet business standards without deep technical input. Expert support is often available to refine or customize designs further, ensuring optimal functionality.
End-to-End Workflow Automation
No-code tools offer comprehensive workflow automation that connects multiple business processes. Users can create complex automations, such as routing approvals, data syncing, or notifications, without writing code.
These platforms use drag-and-drop interfaces combined with pre-built integrations. This enables non-developers to link disparate systems, from CRM to email, in a single automated flow.
One-click build capabilities allow testing and deployment of these workflows quickly. The reduction in manual tasks leads to improved efficiency and fewer errors in operations.
Scalable Infrastructure Support
No-code platforms provide robust, scalable infrastructure supporting growing application demands. Cloud-based architectures allow apps to handle increasing users and data volume without manual intervention.
This scalable infrastructure ensures high availability and performance as business needs evolve. Many solutions manage scaling transparently, so users focus on functionality rather than backend details.
Advanced no-code platforms also offer options for customization and integration with developer tools for future expansion. This flexibility helps companies transition from citizen developers to professional teams without losing application continuity.
Core Capabilities of Low-Code Solutions
Low-code platforms offer several core capabilities that distinguish them from no-code options. These include the ability to incorporate custom code, advanced security protocols, and tools to enhance collaboration among developers. These features facilitate more complex and scalable application development.
Customizable Code Integration
Low-code platforms allow users to embed custom code snippets where pre-built components cannot meet specific needs. This helps address unique business logic or third-party API integration that off-the-shelf modules lack.
Developers can write code in languages like JavaScript, Python, or Java within the platform, enabling flexibility without starting from scratch. It also supports integration with existing enterprise systems, ensuring continuity and reducing migration costs.
This capability is essential for projects requiring fine-tuned control or complex workflows that no-code tools cannot handle. The balance between ease of use and customization helps businesses rapidly develop sophisticated applications.
Advanced Security Features
Security in low-code platforms often complies with industry standards such as GDPR and SOC2. These solutions provide built-in features like role-based access control, data encryption at rest and in transit, and audit trails.
Platforms typically include tools for secure identity management and vulnerability scanning. This safeguards sensitive data and ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR, critical for sectors such as finance and healthcare.
Additionally, some low-code options offer configurable security policies and integration with enterprise security frameworks, enabling organizations to maintain strict control over application access and data transmission.
Developer Collaboration Tools
Low-code platforms encourage teamwork by featuring integrated collaboration tools. These often include shared version control, real-time commenting, and task assignment within the development environment.
Teams can track changes, manage code reviews, and merge contributions smoothly without disrupting the workflow. This reduces bottlenecks between business analysts, developers, and IT staff.
Collaboration dashboards and analytics provide visibility into project progress, resource allocation, and potential issues. This aids management in making informed decisions and aligning development goals with business objectives.
Top Use Cases and User Profiles in 2025
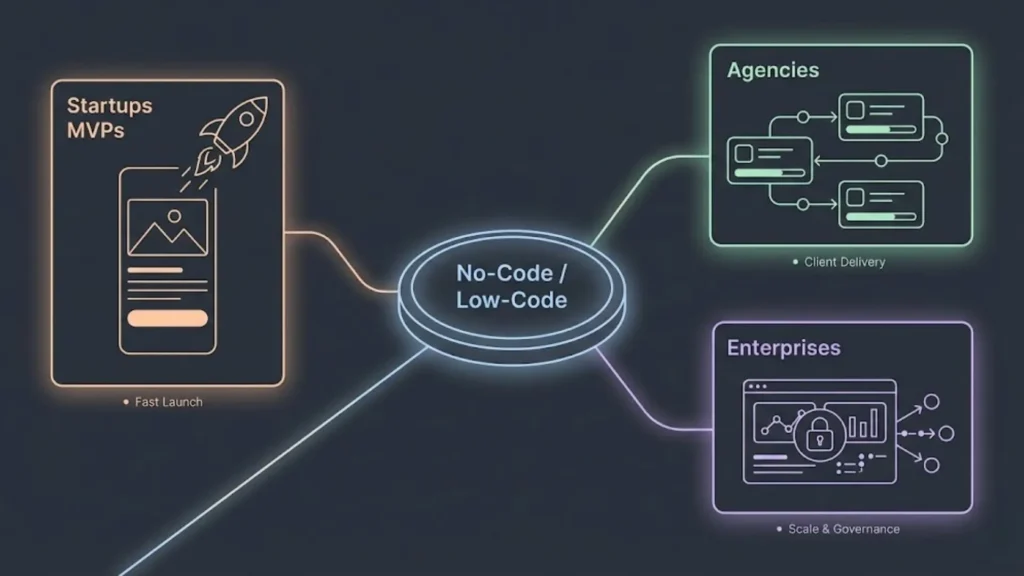
No-code and low-code platforms have distinct strengths that attract different users and projects. Some excel in rapid prototyping, others streamline complex workflows, and many support advanced enterprise requirements. Understanding these helps match the right tool to the right need.
MVP Development for Startups
Founders and solo makers increasingly rely on no-code tools to build minimum viable products (MVPs) quickly. These platforms enable them to test ideas without writing extensive code, reducing initial costs and time to market.
No-code excels in simple apps like landing pages, databases, and basic customer workflows. Startups value drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built integrations that eliminate technical overhead.
However, low-code platforms come into play when MVPs require some custom business logic or user-specific features. This hybrid approach provides both speed and flexibility without full-scale development efforts.
Agency and Freelance Workflows
Agencies and freelancers use no-code and low-code platforms to deliver client projects faster and with less dependency on developers. They handle website builds, internal tools, and marketing automation primarily on no-code platforms due to ease of customization and maintenance.
Low-code platforms support projects needing complex integrations or scalable backends. Agencies working with larger clients or multi-system setups favor these systems for their control and extensibility.
Using these platforms, agencies streamline workflows, manage multiple projects, and reduce delivery timelines. They also empower non-technical clients to manage apps post-deployment, improving client satisfaction.
Enterprise-Level Applications
Large enterprises increasingly adopt low-code platforms for complex applications involving deep integrations, custom logic, and regulatory compliance. These tools allow IT teams to maintain control while accelerating delivery.
Low-code supports dynamic dashboards, ERP integrations, AI-driven features, and multi-user environments, which no-code generally cannot handle.
Enterprise users include business analysts and professional developers who collaborate with citizen developers to build scalable solutions. Security, governance, and performance are key low-code strengths in this space.
How imagine.bo Revolutionizes No-Code in 2025

Imagine.bo streamlines app creation by combining AI technology with expert support, making it accessible for users without coding experience. It simplifies the path from idea to deployment, offers a private beta for early adopters, and integrates smoothly with popular cloud providers. Pricing remains transparent to help businesses plan effectively.
Idea-to-App Process
Imagine.bo starts by letting users describe their app idea in plain language. Its AI then generates a detailed blueprint outlining the app’s structure and features. This reduces ambiguity and accelerates development planning.
Users can launch their app with a single click using the platform’s one-click build feature. This automation handles coding tasks, infrastructure setup, and basic testing without manual coding. It supports deployment on AWS, GCP, and Vercel, ensuring reliable performance and scalability.
The process emphasizes speed and ease, empowering entrepreneurs to focus on functionality rather than technical complexity.
Private Beta Overview
Imagine.bo operates a private beta phase to refine its tools and gather user feedback. During this period, early users can test the platform’s capabilities under real-world conditions.
Access to the private beta includes direct engagement with the Imagine.bo team to report issues, request features, or receive guidance. This collaboration helps tailor the product to user needs while maintaining stability and performance standards.
The private beta also offers early adopters benefits like preferential pricing and priority support, encouraging adoption and continuous improvement.
Deployment and Expert Assistance
Deployment on Imagine.bo is designed to be seamless and flexible. The platform supports major cloud services, including AWS, GCP, and Vercel, giving users options based on cost and technical requirements.
In addition to AI automation, users receive expert backup from seasoned developers who review critical parts of the build and assist with customization or troubleshooting. This hybrid model ensures quality without requiring users to write code themselves.
Pricing is clear and based on usage, allowing startups and businesses to manage expenses while scaling their applications confidently.
Evaluating Security, Scalability, and Compliance
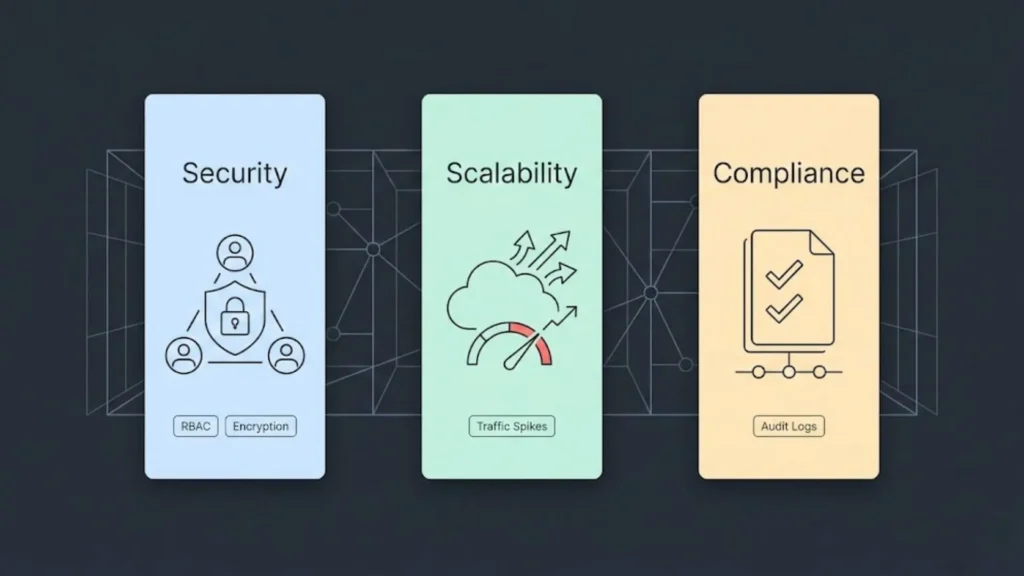
Security, scalability, and regulatory compliance are critical factors when choosing between no-code and low-code platforms. Each type has unique approaches to managing these aspects that influence their suitability for different business needs.
Built-In Security Protocols
No-code and low-code platforms offer predefined security features to protect applications, but visibility into underlying systems is often limited. Both rely on platform providers to manage core security controls such as data encryption, authentication, and access management.
Low-code platforms usually provide deeper customization for implementing advanced security measures since they allow some coding. This flexibility enables integration of specific protocols like SOC2 standards or custom encryption routines.
No-code tools tend to prioritize ease of use over complex security configurations, which may restrict their ability to meet stringent security frameworks like GDPR. However, many platforms continuously improve compliance features to help handle data privacy requirements automatically.
Handling Traffic Spikes
Scalability is a major consideration for applications expected to experience fluctuating or high traffic volumes. No-code solutions generally include scalable infrastructure by design, handling load increases without requiring significant changes to workflows or architecture.
Low-code platforms offer scalability but often depend on how well developers optimize the underlying code and infrastructure. This can make scaling more resource-intensive and potentially slower compared to no-code.
Both platforms support cloud deployment options, but no-code’s abstraction layer typically simplifies horizontal scaling. Low-code allows more control but demands technical expertise to ensure the system performs well under heavy loads.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations like GDPR and SOC2 is essential for many businesses using no-code or low-code platforms. These platforms provide varying levels of support to help meet legal and industry standards.
No-code platforms automate many compliance-related tasks but might lack transparency concerning data processing, which could be a concern in highly regulated sectors. Low-code solutions, given their flexibility, allow businesses to tailor compliance processes more precisely.
Choosing the right platform involves assessing whether built-in compliance features align with specific organizational and regulatory requirements, including data residency and audit needs. Frequent updates from platform providers help keep controls current with evolving laws.
Pricing Models and Return on Investment
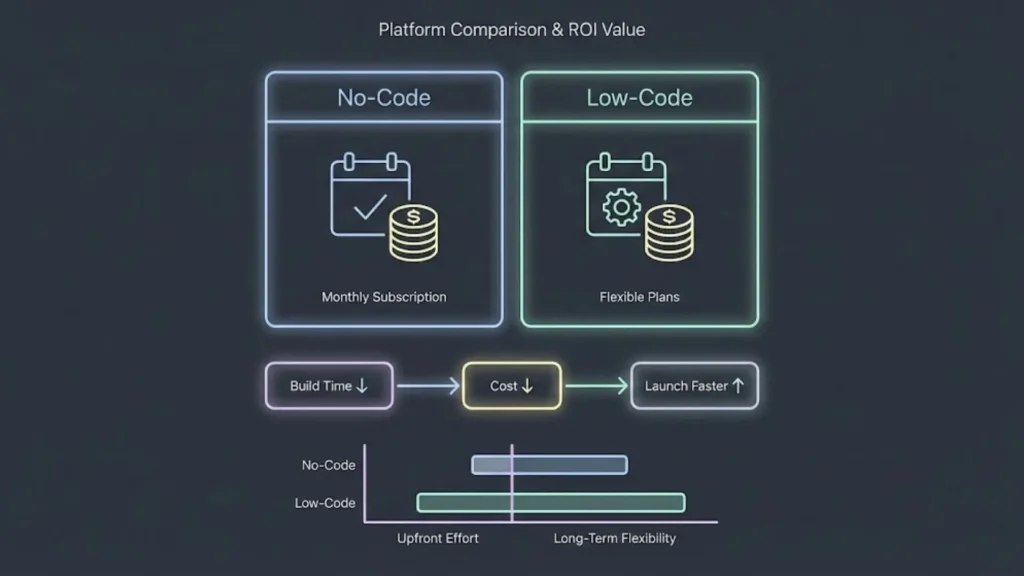
Pricing for no-code and low-code platforms generally follows subscription models, which allow users to pay based on their usage and feature needs. Understanding the cost differences and evaluating ROI is essential, especially for businesses balancing upfront expenses with long-term benefits.
Subscription Pricing
Most no-code and low-code platforms operate on subscription-based pricing. Fees vary depending on the number of users, access to advanced features, and customization options. No-code plans typically start lower, often ranging from monthly subscriptions of $50 to several hundred dollars for basic tiers.
Low-code platforms usually require higher subscription fees due to more complex features and scalability, often starting around $500 per month for small teams. These platforms offer tiered pricing with clear plans, allowing businesses to choose packages based on project size and integration requirements.
Clear pricing structures and paid plans help organizations budget effectively and scale usage without large upfront costs. Subscriptions reduce financial risks but require ongoing commitment to maintain features and support.
Cost Comparison: No-Code vs Low-Code
No-code platforms generally cost between $30,000 and $100,000 annually depending on deployment scale and functionality. Their lower price point suits rapid prototyping and simple application needs.
Low-code platforms range from approximately $100,000 to $300,000 annually, reflecting their greater customization and integration capabilities. Despite higher initial expenditures, these platforms often lead to better scalability.
Traditional software development costs exceed these ranges significantly, sometimes several times higher. A key cost advantage of no-code and low-code is the reduction in manual coding hours, accelerating development and cutting labor costs.
| Platform Type | Typical Annual Cost Range | Key Cost Driver |
|---|---|---|
| No-Code | $30,000 – $100,000 | Simplicity, prebuilt components |
| Low-Code | $100,000 – $300,000 | Customization, scalability |
Assessing Value for Agencies and Startups
For agencies and startups, no-code and low-code tools offer fast deployment and cost efficiency. No-code platforms enable quick delivery of MVPs with minimal technical overhead, reducing time-to-market and initial investment.
Low-code tools provide more flexibility to scale applications and integrate complex workflows, making them valuable for growing startups that anticipate evolving requirements. Agencies benefit from low-code platforms by offering tailored solutions while maintaining efficient development cycles.
Return on investment is often measured by how quickly projects reach production and begin generating revenue or savings. Low-code adoption can deliver ROI improvements of over 200% within three years by lowering development expenses and maintenance.
In both cases, selecting platforms with clear pricing and flexible paid plans can prevent hidden costs, supporting predictable budgeting and strategic growth.
Selecting the Right Platform for Your Needs
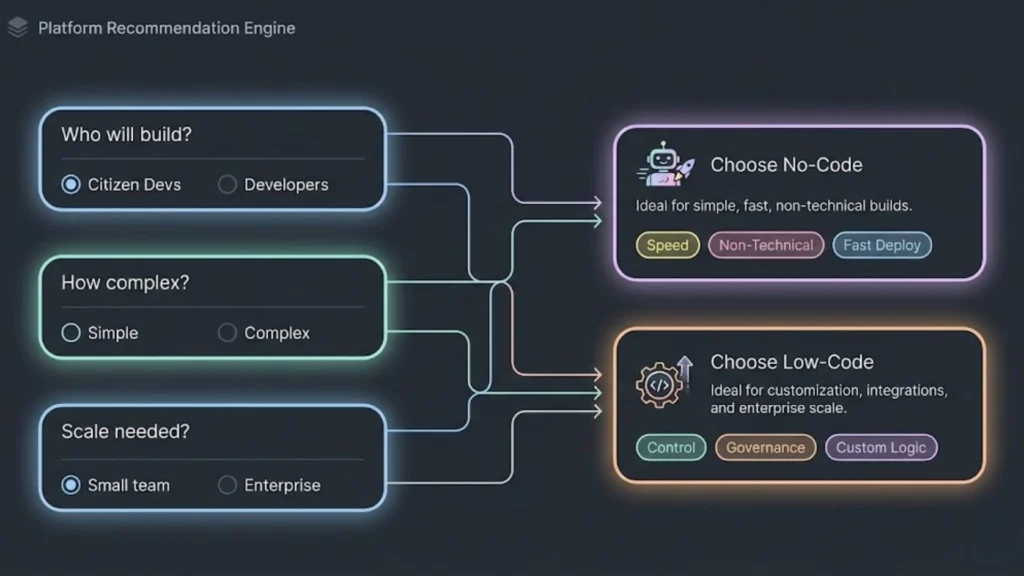
Choosing between no-code and low-code platforms requires evaluating project complexity, user experience, and long-term goals. The right choice depends on aligning technical features with project demands, ensuring accessible onboarding and reliable support, and considering future scalability and innovation.
Matching Platform Features to Projects
No-code platforms are best for straightforward, quick-deployment projects with limited technical complexity. They offer drag-and-drop interfaces and predefined templates designed to accelerate simple workflows and minimize coding.
Low-code platforms suit projects needing customization, scalability, and integration with existing systems. Their flexibility allows developers to write custom code where necessary, supporting complex business logic and large-scale applications.
Consider this when choosing:
| Feature | No-Code | Low-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity Handling | Basic | Advanced |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive |
| Development Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Integration Options | Simple | Broad |
Onboarding and Support Options
Effective onboarding accelerates adoption and reduces time to market. Many platforms provide tutorials, templates, and guided workflows to assist new users.
Expert support, including live chat, forums, and dedicated technical assistance, is critical for troubleshooting and advancing platform use. Platforms in private beta phases often offer personalized onboarding but may have limited public documentation. Users should verify available support channels before committing.
Future Outlook for No-Code and Low-Code
No-code platforms continue to evolve with enhanced AI-driven automation and broader applicability beyond small projects. They are opening software development to non-technical teams more than ever.
Low-code platforms focus on scalability, integration with enterprise systems, and enabling professional developers to accelerate complex application delivery. Both models emphasize increasing collaboration between business and IT roles.
Organizations should watch for emerging features like AI-assisted coding, expanding marketplace plugins, and stronger security frameworks in both categories. For more on where this technology is heading, check out the Future Outlook for No-Code.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





