Building a high-quality no-code app in just 10 days requires shifting your focus from perfection to functional utility. Success lies in ruthless prioritization: spend the first 48 hours launching your idea by mapping core user flows. By day five, aim for a no-code MVP that solves one specific problem. To avoid common pitfalls, follow a proven no-code action plan to ensure your transition from a raw concept to a live, scalable tool is both fast and secure.
Imagine building an app without the usual pain
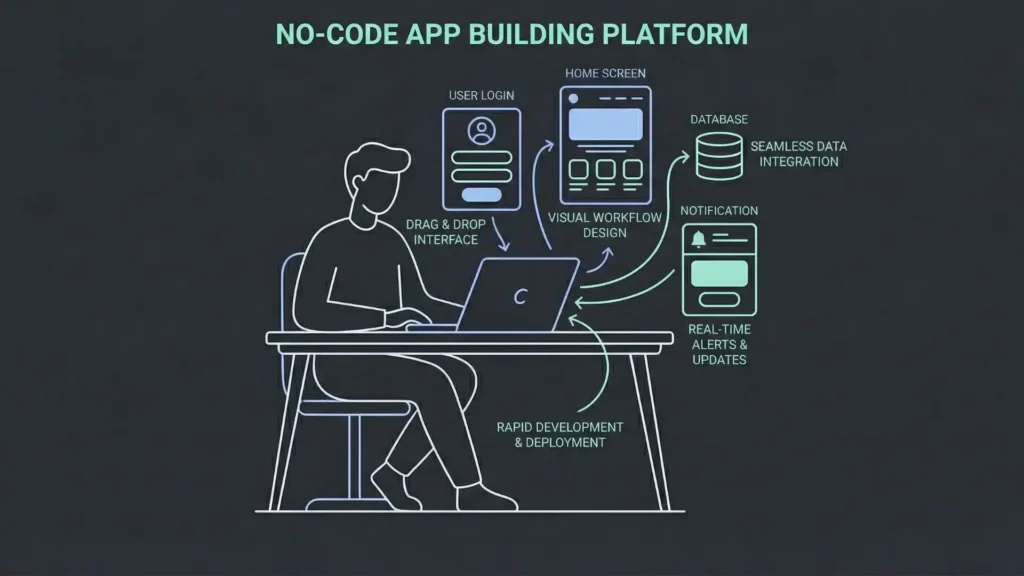
You have an app idea. Maybe it is a customer portal you wish existed, a booking tool for your small business, or a niche product that solves one specific problem.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildIn a traditional software setup, the first obstacle isn’t actually building. It is everything around the building process: hiring hurdles, long timelines, endless back-and-forth, and budget approvals. Worst of all is the constant risk that you will spend six months and $50,000 only to learn that users didn’t actually want the thing.
No-code flips that equation.
Instead of waiting for engineering cycles, you can move from a concept to a working MVP in days. We are not talking about a prototype that only looks good in a demo. We mean something real that users can log into, use, and provide feedback on. This guide walks through a practical 10-day sprint to launch a no-code app in 10 days. It is designed for founders and operators who want speed without sacrificing quality.
The no-code revolution: Why “now” is different
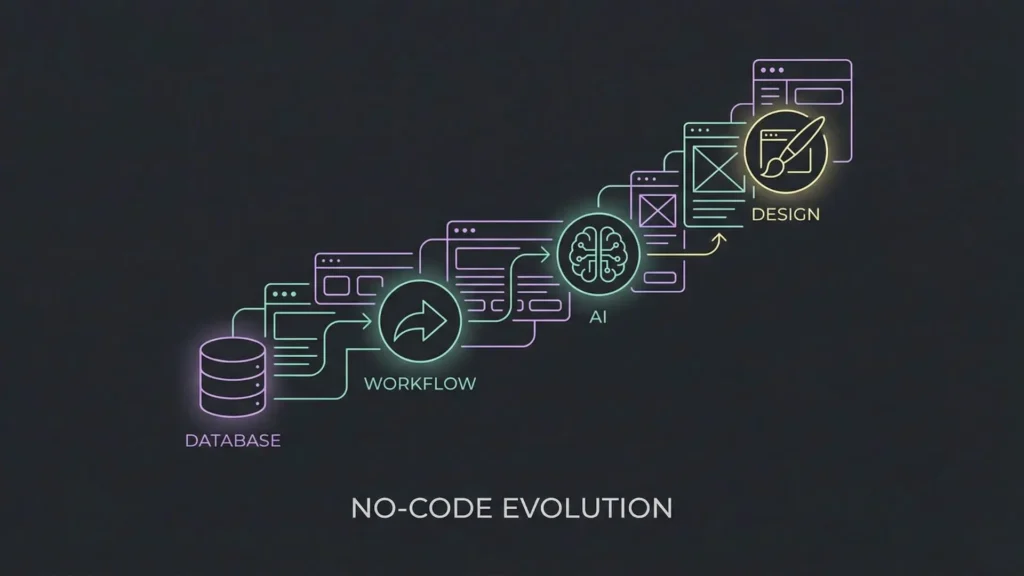
No-code has been around for a while, but the landscape has shifted. We have moved past simple website builders into an era of sophisticated no-code app development.
The outcome is simple: you can build faster and get closer to production standards than ever before. This shift is driven by three main factors:
- Mature Platforms: Modern tools offer robust databases, complex workflows, and secure authentication.
- Better UX Expectations: You no longer have to compromise on design. Responsive tools and pre-built components make apps look professional out of the box.
- AI Assistance: AI is now the “co-pilot” for planning, logic, and troubleshooting, removing the technical barriers that used to stall non-technical builders.
This means you can enjoy faster validation with less risk. Your first version doesn’t need a large team, which makes experimentation financially possible. If the market shifts, you can adapt in days rather than quarters. Many non-technical founders are building products today that would have required a full engineering team just three years ago.
The Strategic Shortcut: Optimizing Your Build
To successfully launch MVP versions within this tight window, you must master the “80/20 of Logic.” This means identifying the single most important workflow the one that delivers the actual value and making it bulletproof while keeping everything else secondary. If your app connects buyers and sellers, spend your energy on the transaction flow, not the “About Us” page. Speed in no-code comes from saying “not now” to 90% of your ideas so that the remaining 10% can be exceptional. True efficiency isn’t just about building faster; it is about choosing the best no-code tools to launch your startup fast and ignoring the features that don’t serve the core mission.
Days 1–3: Validation, Architecture, and Platform Selection
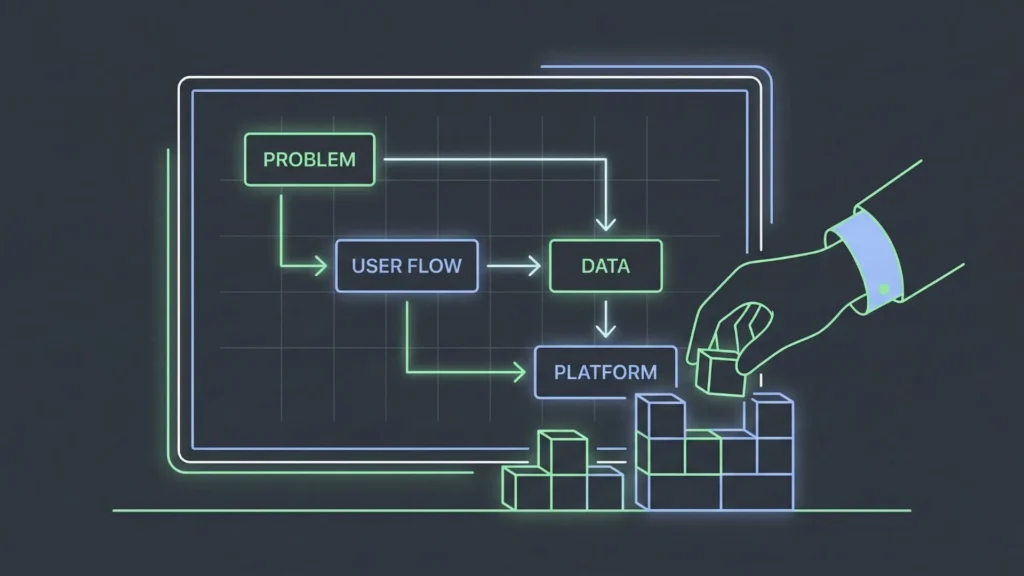
Day 1: Define the problem and the MVP
Start with one sentence: “This app helps [specific user] solve [specific problem] by [specific outcome].” For example: “This app helps freelance designers track client approvals so projects do not stall.”
For a 10-day sprint, your MVP must be brutally small. Use the Core Pain Filter: Does this feature solve the primary pain? Write 5 to 10 user stories using the “As a [user], I want to [action], so that [benefit]” structure. If you need inspiration, look at these 10 profitable no-code app ideas to see how simple a successful MVP can be.
Day 2: Map user flows and data structure
Mapping your flow saves hours of rework later. Draw the path: Landing → Sign up → Dashboard → Primary action → Success. Next, draft your data model. List your core data types (e.g., Users, Appointments, Services). A clean data model prevents weird “hacks” during the build phase.
Day 3: Pick the right platform
Do not choose based on hype. Choose based on fit. Ask: Is it a web app or mobile-first? How complex is the database? What integrations (payments, email, CRM) are non-negotiable? For a no-code sprint, the learning curve of the tool is just as important as its features. You can compare different approaches in our no-code vs low-code for startups guide.
Days 4–6: Foundation, UI Design, and Data Connectivity
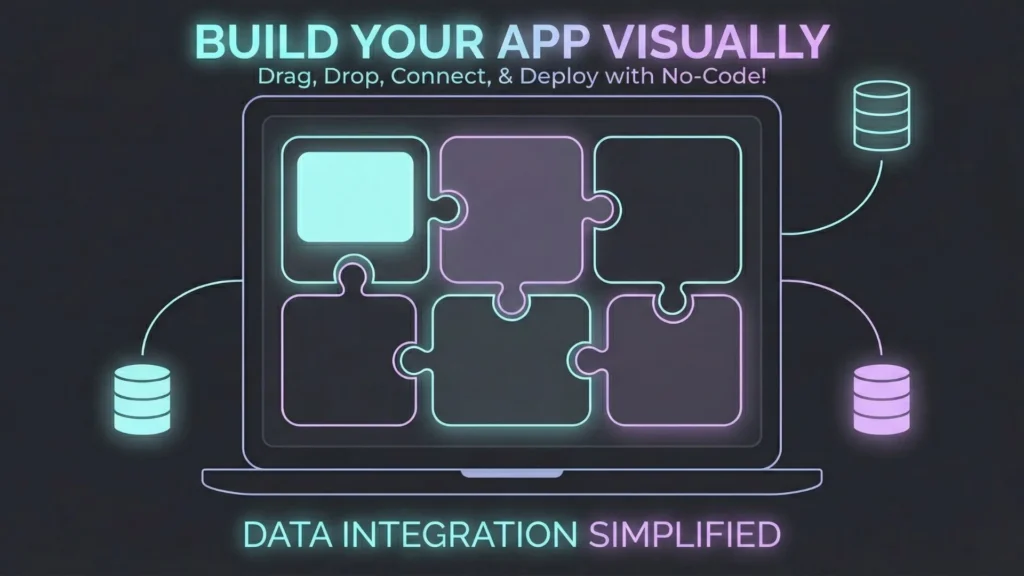
Day 4: Set up the environment
Goal: remove all friction before the build begins. Create your accounts, set up your database tables, and configure authentication. If you need a brand kit, prepare your logo and colors now. By the end of Day 4, your “digital construction site” should be ready for the first brick.
Day 5: Build UI screens
Focus on “clear and usable” over “pixel perfect.” Build your login, dashboard, primary action screen, and settings. Stick to one font family and a consistent button style to keep the interface clean. Use placeholders where necessary, but ensure the layout reflects the actual user journey mapped on Day 2.
Day 6: Connect UI to data (CRUD)
This is where you build an MVP fast. Make the app functional by enabling CRUD operations: Create (adding records), Read (viewing lists), Update (editing info), and Delete (removing data). Once your buttons actually move data into your database, the “app” officially comes to life. If you are struggling with this, follow a step-by-step guide to building your MVP.
Days 7–10: Logic, Security, QA, and Launch
Day 7: Workflows and logic
Workflows are the behavior of your app. When a user submits a form, set up the triggers that send confirmation emails, update internal statuses, or redirect users to success pages. Add basic guardrails like required fields to prevent users from accidentally entering “bad” data. You can learn more about automating workflows without writing code to make your app feel like magic.
Day 8: Permissions and privacy
Permissions are not optional. Ensure users can only see their own records. Test this like a skeptic: Can you guess another user’s URL and see their data? Most no-code app development platforms handle this well, but you must configure the privacy rules intentionally. Check out our no-code app security best practices for a full checklist.
Day 9: Testing and refinement
Treat this as a Quality Assurance day. Do not add new features. Test the “Happy Path” from signup to success. Then, test the “Edge Cases” like blank inputs or slow connections. Check the app on desktop and mobile. Finally, verify that your analytics are tracking signups and key actions correctly.
Day 10: Launch and post-launch plan
Launch MVP checklist: Connect your custom domain, update SEO meta descriptions, and check that email delivery is working. Once live, your goal shifts to listening. Spend the first week reviewing analytics and talking to users to find the top five friction points.
Where AI-first no-code fits

While the 10-day sprint is effective, the “tool chaos” of managing multiple platforms can be overwhelming. This is where AI-first platforms are changing the game by consolidating the stack.
Imagine.bo is a prime example of this evolution. Rather than stitching together fragmented tools, it functions as an AI-driven, end-to-end builder. You describe your product in plain English, and its AI reasoning engine helps generate the architecture, workflows, and system logic.
In a no-code sprint, this platform reduces the time spent on “translation” the gap between what you want and how the database should look. It follows a 5-step workflow that covers everything from business goals to cloud-native deployment on AWS or Google Cloud. Because it emphasizes SDE-level engineering standards, you avoid the “duct-tape” feel common in early MVPs. It is built for scale, supporting up to 1,000 transactions per second and offering enterprise-grade security readiness like GDPR and SOC2. For those who need a custom touch, there is even the option for human developer support to polish the AI-generated output. It is essentially an AI no-code app builder designed for professional results.
Common mistakes to avoid in a no-code sprint

Even with the best tools, it is easy to trip up. Here are the most frequent pitfalls we see builders make:
- Scope Creep: Trying to build a “version 2” before “version 1” is live. If it isn’t essential for the first user, cut it.
- Over-designing: Spending two days on a logo instead of the data model. Use a template and move on.
- Weak Data Models: If your database is messy, your workflows will break. Spend the extra time on Day 2.
- Ignoring Permissions: Thinking “I’ll fix security later” is a recipe for a data breach. Lock down your privacy rules on Day 8.
- Forgetting Mobile: Ensure you design for mobile and desktop users simultaneously.
Post-launch iteration and metrics
Launching is just the beginning of the no-code app development journey. Once the app is live, focus on these three metrics:
- Activation: Did the user perform the core action (e.g., create their first invoice)?
- Retention: Do they come back after the first day?
- Feedback Loops: Are you getting qualitative data on what is confusing?
Use a simple “Fix, Add, Change” cycle. Every week, fix two bugs, add one small enhancement, and change one UI element based on user friction. If you want to dive deeper into scaling, check out our product-market fit framework for no-code.
FAQs
Can you really build a no-code app in 10 days?
Yes, provided you are disciplined about scope. A no-code sprint is for an MVP, not a complex enterprise system. If you focus on one core problem, 10 days is plenty.
What is the best no-code platform?
There is no single “best” tool. The right choice depends on whether you need a web app, a mobile app, or a heavy data-processing tool. You can find many free AI app builders to start your journey without upfront costs.
Is no-code secure enough for real users?
Absolutely. Most modern platforms have high security standards. However, security is a shared responsibility. You must set up your own privacy rules and permissions correctly.
When should I use an AI no-code app builder?
Use an AI no-code app builder when you want to move faster than manual dragging-and-dropping allows, or when you want to ensure your app’s architecture is scalable from day one.
Do I need to know anything about databases?
You don’t need to write code, but understanding how “objects” and “fields” relate will make your build much smoother.
What happens if I outgrow my no-code tool?
Many modern platforms allow you to export data or connect via API. Some, like Imagine.bo, use standard cloud architectures that make the transition to traditional code easier if ever needed.
Conclusion
A no-code app in 10 days is not a myth; it is a product discipline exercise. By planning tightly, shipping only the essentials, and testing hard, you can bypass the traditional months of development. No-code gives you speed, and AI-first platforms reduce the friction of execution even further.
Ten days is enough time to learn whether your idea deserves ten months of your life. Stop sitting on the idea and start the sprint.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





