The barrier to entry for building software has never been lower. In the past, launching an artificial intelligence application required a team of specialized engineers, months of development, and a massive budget. Today, the landscape has shifted. We are seeing a surge in platforms that allow founders and product teams to prototype AI solutions in days.
However, a prototype is not a product.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildThe real challenge for modern businesses is not just building an AI application but ensuring it is production-ready. This means the system must handle thousands of concurrent users, manage vast amounts of data securely, and maintain low latency without crashing. This is where the concept of the scalability of no-code AI applications becomes critical. It represents the bridge between a fragile proof-of-concept and a robust, scalable business asset.
This guide explores the engineering reality behind scaling no-code applications. We will move beyond the basics of drag-and-drop interfaces to discuss infrastructure, data pipelines, security, and the architectural decisions required to build for the long term.
Understanding the No-Code AI Landscape
To navigate the scaling process, we must first define the current state of the technology. No-code AI refers to development platforms that allow users to build applications using visual interfaces while leveraging pre-trained machine learning models or connecting to AI APIs (like OpenAI or Anthropic).
Define No-Code AI Clearly
At its core, this technology abstracts the complexity of coding. Instead of writing Python scripts to train a neural network or configuring Docker containers for deployment, users interact with logic flows and visual editors. The “AI” component usually comes in two flavors:
- Generative AI integration: Connecting applications to Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate text, images, or code.
- Predictive AI: Using built-in models to analyze data, predict trends, or classify information without manual model training.
Advantages for Founders and Teams
The primary advantage is speed. Founders can iterate on product-market fit without waiting on a backlog of engineering tickets. For non-technical teams, it democratizes innovation. Marketing teams can build sentiment analysis tools, and operations teams can automate complex workflows. This agility is vital in the early stages of a company.
Real-World Adoption Context
Adoption has moved beyond hobbyists. Enterprises are now using no-code AI platforms to deploy internal tools, customer-facing chatbots, and data processing units. The market has matured, and the expectation is no longer just “does it work?” but rather “can it scale?”
Why Scaling No-Code AI Is Different
Scaling a traditional software application involves known variables. You optimize code, add load balancers, and increase server capacity. Scaling no-code applications presents unique challenges because you are often working within the constraints of the platform you chose.
Data Volume and Performance Challenges
When an application moves from 100 users to 100,000 users, the data volume explodes. In a traditional environment, engineers would optimize database queries to handle this load. In a no-code environment, inefficient logic flows can become major bottlenecks. If a visual workflow triggers a loop that queries the database 50 times per user action, the system will grind to a halt under load. Understanding how your platform handles data fetching and caching is essential for maintaining performance.
Model Optimization Limitations
In custom development, engineers can fine-tune AI models to reduce latency. They might quantize a model to make it smaller or use a specific hardware accelerator. In a no-code environment, you often consume AI as a service via an API. This means you have less control over the inference speed. Scaling here requires smart architectural choices, such as cost optimization for AI APIs, which involves caching common AI responses or using smaller, faster models for simple tasks to reduce the load on the primary AI engine.
Integration and Infrastructure Bottlenecks
No-code tools rely heavily on integrations. You might use one tool for the frontend, another for the database, and a third for the AI logic. When you scale, these connection points become risks. API rate limits can be hit unexpectedly, causing the application to fail for users. Furthermore, relying on multiple third-party services introduces latency. Every time data hops from one service to another, milliseconds are added to the total request time.
No-Code vs Traditional AI Development
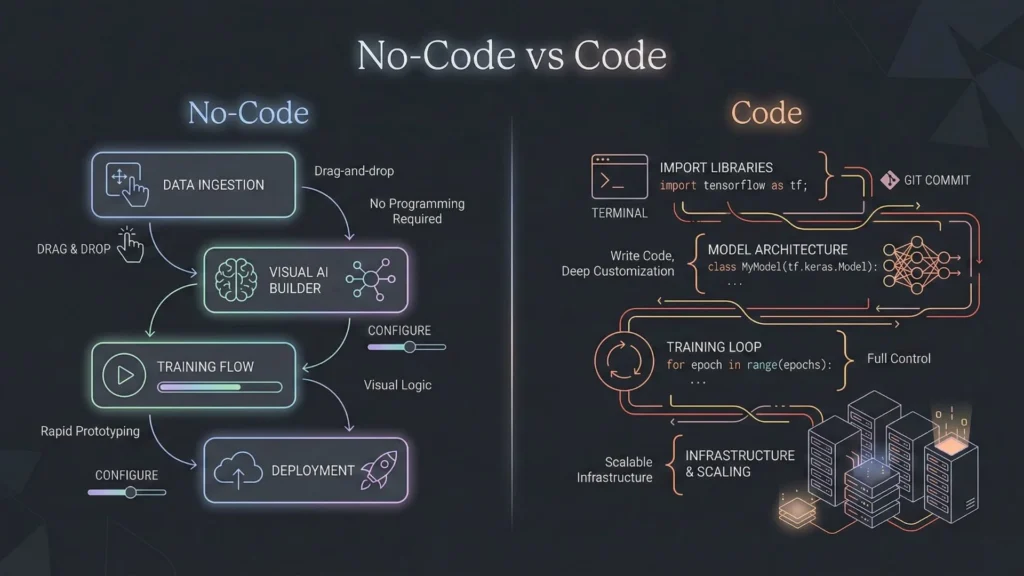
Founders often debate whether to stick with no-code or hire a development team. The answer often lies in the specific scalability requirements of the project.
Scalability Comparison
Traditional development offers infinite scalability, provided you have the engineering talent to build it. You can control every byte of memory and every CPU cycle. When comparing no-code vs. traditional development, the former traditionally hit a ceiling where the platform’s constraints limited growth. However, this gap is closing. Modern enterprise-grade no-code platforms are built on top of the same scalable cloud infrastructure (AWS, Google Cloud) that traditional developers use. The scalability now depends more on the platform’s architecture than the “no-code” nature itself.
When No-Code Works Best
No-code excels when time-to-market is the priority and when the application logic fits standard patterns (e.g., marketplaces, SaaS tools, content platforms). It is also the superior choice for internal tools where engineering resources are better spent elsewhere.
Hybrid Approaches for Long-Term Growth
Many successful companies adopt a hybrid model. They use no-code AI platforms for the core application logic and user interface while offloading heavy data processing or proprietary AI model training to custom code services. This allows them to move fast without being locked into a single ecosystem.
Infrastructure Choices for Production-Ready No-Code AI
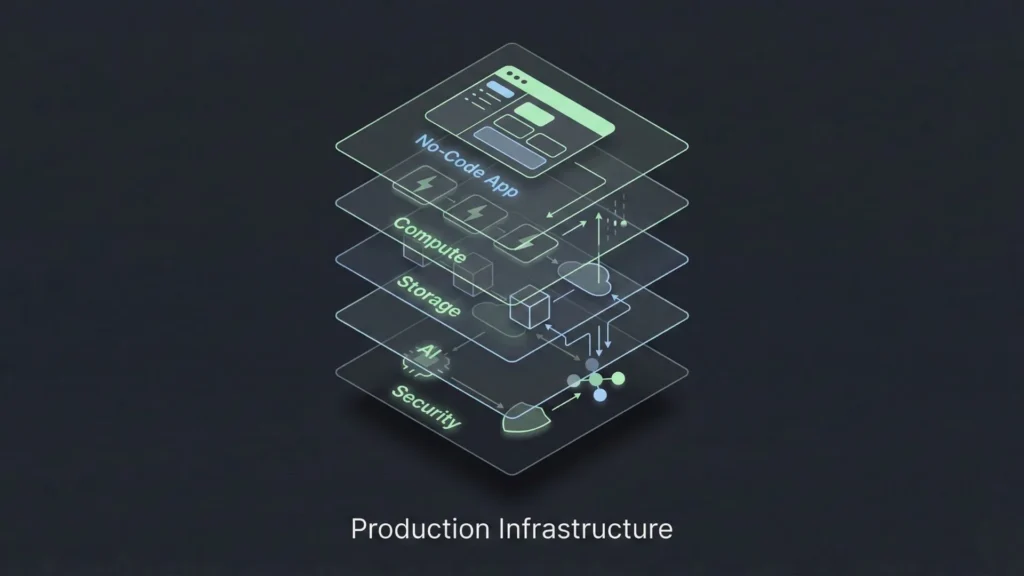
To achieve production-ready no-code AI, you must look under the hood. Even if you aren’t writing code, you are making infrastructure decisions based on the platform you select.
Serverless Architectures
Serverless computing is the backbone of scalable no-code. In this model, the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation of machine resources. Code is executed based on events (like a user clicking a button). This is ideal for AI applications because it scales to zero when not in use and scales up instantly during traffic spikes. When evaluating platforms, prioritize those that utilize scalable SaaS architecture to ensure you aren’t paying for idle servers.
Containerization and Orchestration
While users may not see it, the best no-code platforms use technologies like Docker and Kubernetes. These tools package applications into “containers” that can run anywhere. This ensures consistency. If a platform creates a container for your application, it means your app is isolated. If another user on the same platform crashes their app, yours remains unaffected. This isolation is non-negotiable for production-grade systems.
Cloud Platform Considerations
Where does the data live? Production-ready systems must offer transparency regarding data residency. If your users are in Europe, you need a platform that can store data in EU servers to comply with GDPR. The underlying cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP) matters for reliability and uptime guarantees.
Data Management Strategies at Scale

AI eats data. Managing that data efficiently is the difference between a snappy application and a sluggish one.
Handling Large Datasets in No-Code Tools
A common mistake is trying to load entire datasets into the user’s browser. As you scale, you must implement server-side pagination. This means the server only sends the 20 or 50 records the user is currently looking at, rather than the 50,000 records in the database. Ensure your chosen platform supports complex querying and indexing so that finding a specific record remains fast regardless of database size.
Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering
Raw data is rarely ready for AI processing. It needs cleaning and formatting. In a scalable architecture, this preprocessing should happen asynchronously. For example, if a user uploads a PDF to be analyzed by AI, the system should acknowledge the upload immediately and process the file in the background, notifying the user when it is done. This prevents the user interface from freezing while the heavy lifting happens.
Designing Reliable Data Pipelines
Data needs to flow reliably between your database, your AI models, and your frontend. A production-ready pipeline includes retry logic. If the AI API times out, the system should automatically try again or queue the request for later. Tools that allow you to visualize your data effortlessly often have built-in connectors that handle these pipelines, but it is crucial to verify that they support error handling mechanisms.
Building Reliable and Monitorable No-Code AI Systems
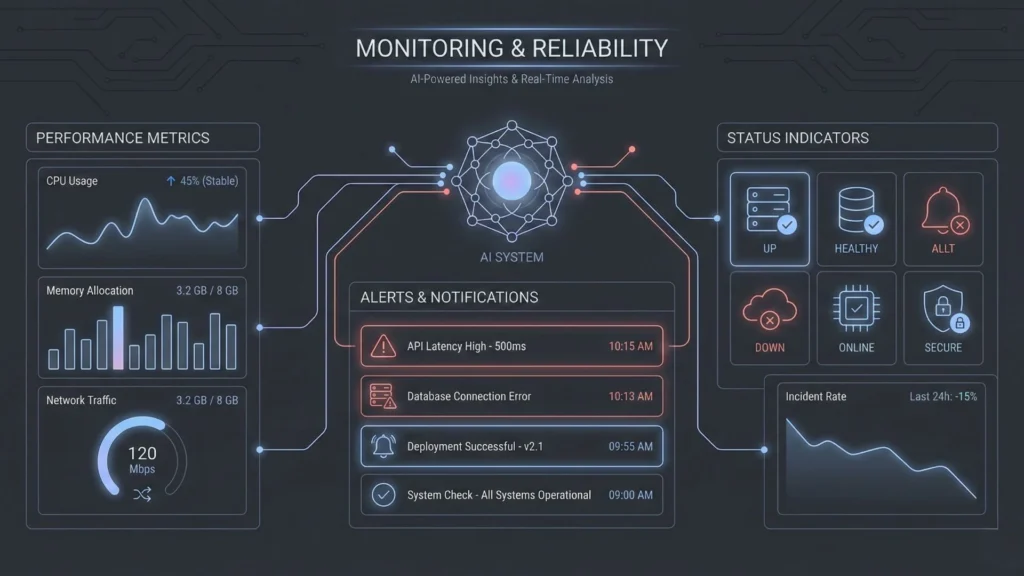
You cannot fix what you cannot see. Observability is often an afterthought in no-code, but it is critical for production.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
You need dashboards that show more than just “active users.” You need to track AI token usage, API error rates, and average response times. If the error rate spikes, the product team should be alerted immediately via email or Slack. This allows you to address issues before users flood your support channels.
Error Handling and Recovery Strategies
How does your app behave when things go wrong? If the AI returns a hallucination or a nonsense answer, do you show it to the user? Robust systems include validation steps. For example, the output of an LLM can be passed through a second, smaller model or a regex filter to ensure it meets quality standards before being displayed.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance
Scalability is impossible without security. Enterprise clients will demand SOC2 compliance, data encryption at rest and in transit, and strict access controls. You must ensure that the platform you build on inherits these security standards. Implementing no-code app security best practices includes setting up Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure that junior team members cannot accidentally delete production databases or expose sensitive user data.
Testing and Deployment Best Practices
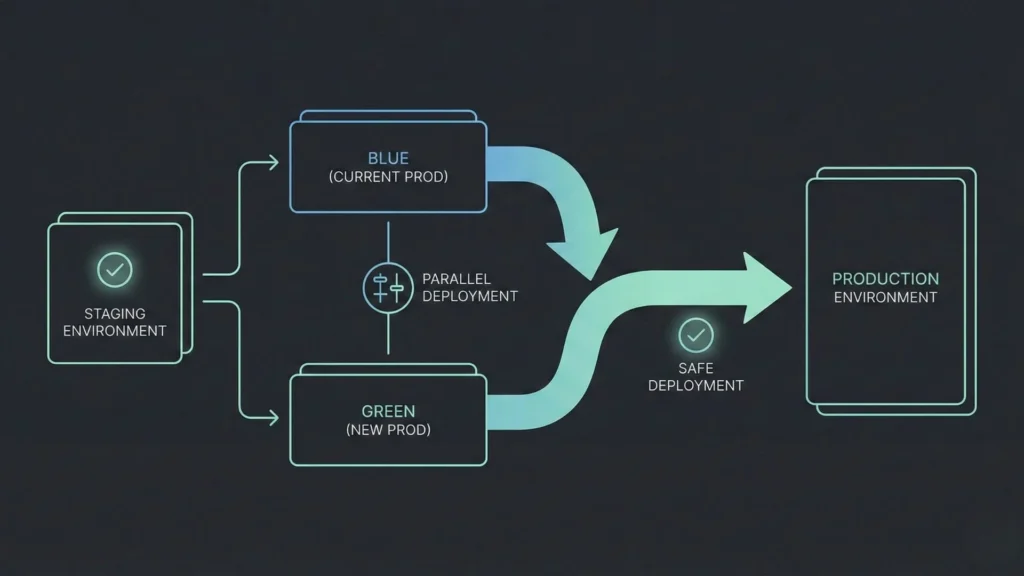
Moving from “it works on my screen” to “it works for everyone” requires discipline.
CI/CD for No-Code AI
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is a standard in software engineering that is making its way to no-code. It involves version control. You should never make changes directly to your live application. Instead, use a versioning system where changes are saved, reviewed, and then “pushed” to the live environment.
Environment-Specific Testing
You need at least two distinct environments: Staging and Production. Staging is where you test new AI prompts, new logic flows, and database changes. Only once they are verified in Staging should they be deployed to Production. This separation prevents accidental breakage of the live app.
Reducing Deployment Risks and Downtime
Deployments should be zero-downtime. Users currently on the app shouldn’t notice that an update has happened. This is achieved through strategies like “blue-green deployment,” where the new version is spun up alongside the old one, and traffic is gradually shifted over. Utilizing creative debugging strategies during the staging phase can help catch edge cases before they affect live users, ensuring a smoother transition during these deployments.
Incorporating Advanced Engineering Standards: The Role of Specialized Platforms

As we analyze the requirements for scaling infrastructure, security, pipelines, and compliance it becomes clear that cobbling together disjointed tools is risky. This is where the next generation of platforms is shifting the paradigm.
There is a growing class of solutions designed to bridge the gap between no-code ease and SDE (Software Development Engineer) quality standards. A prime example of this evolution is Imagine.bo.
Imagine.bo distinguishes itself by focusing on the “production-ready” aspect of creation. While many tools stop at the prototype phase, Imagine.bo is architected to deliver applications that adhere to high-level engineering standards from day one. It handles the heavy lifting of server management, security protocols, and scalable architecture automatically.
For a founder or product manager, this means the ability to build and deploy enterprise-grade AI apps without worrying about the fragile integration points discussed earlier. The platform provides end-to-end ownership, meaning you aren’t just renting a visualization layer; you are building on a foundation designed for performance. By combining human creativity with AI-assisted logic generation, it allows teams to deploy systems that are secure, fast, and capable of handling enterprise-level traffic without needing a DevOps team on standby.
Understanding how Imagine.bo works reveals a focus on generating clean, efficient backend logic that rivals handwritten code, which is often the deciding factor in whether a project successfully scales or stalls due to technical debt.
Real-World Scaling Examples
To visualize success, let us look at how these principles apply in practice.
Customer Service Automation Use Case
A mid-sized e-commerce company implemented a no-code AI chatbot. Initially, it worked fine. But on Black Friday, traffic spiked 10x. The system slowed down because every chat message triggered a direct API call to the LLM.
- The Fix: They implemented a caching layer. Common questions like “Where is my order?” were answered by a simple lookup database rather than the expensive AI model. This scenario highlights the debate of AI chatbot vs. human support, where the hybrid approach of automated caching and AI escalation proved most effective for high-volume periods.
Fraud Detection at Scale
A fintech startup used no-code tools to flag suspicious transactions. As they grew, the latency of checking every transaction became too high.
- The Fix: They adopted an asynchronous architecture. The transaction goes through immediately, and the AI analyzes it in the background (seconds later). If fraud is detected, the account is frozen retrospectively. This kept the user experience fast while maintaining security.
Key Lessons from Successful Projects
- Start simple: Don’t over-engineer the V1.
- Monitor everything: You cannot scale what you do not measure.
- Choose the right foundation: Migrating platforms when you have 10,000 users is painful. Start with a platform that supports SDE-level standards.
Future Trends in No-Code AI Scaling
The landscape is evolving rapidly. Here is what is on the horizon.
Edge Computing
We are moving toward running smaller AI models directly on the user’s device (browser or phone) rather than in the cloud. This reduces server costs to near zero and eliminates latency. No-code platforms will soon offer “Deploy to Edge” options.
Model Optimization and AutoML
Future platforms will automatically optimize your AI calls. They will analyze your prompts and data, then select the cheapest and fastest model that can do the job, switching between GPT-4, Claude, or open-source models dynamically without you needing to configure anything.
Serverless and Emerging Cloud Technologies
The abstraction layer will get thicker. Users will simply define “outcomes,” and the platform will provision the necessary vector databases, GPU clusters, and API gateways globally. This aligns with the future of app development, where the line between engineer and creator blurs entirely, offering enterprise power with consumer simplicity.
Conclusion
Scaling no-code AI applications is no longer a theoretical experiment; it is a viable business strategy. The gap between “code” and “no-code” is narrowing, not because code is going away, but because no-code platforms are adopting the rigorous engineering standards of traditional development.
By focusing on robust infrastructure, efficient data management, and strict security protocols, founders can build systems that do not just survive but thrive at scale. The tools are ready. Start your free production-ready build today and ensure your growth isn’t limited by your tech stack.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





