The line between a conceptual idea and a deployed application is blurring at an unprecedented speed. For decades, software development has been a craft of deliberate, manual precision — translating human logic into machine-readable syntax, line by painstaking line.
Today, that entire paradigm is being fundamentally rewritten by the advent of generative AI. We have officially entered the new era of AI-powered app development. This transformation is moving us from a world of manual coding to one of conversational orchestration.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildIn this guide, we will explore how the humble text prompt has become the ultimate force multiplier for developers and founders alike. We will dive deep into the tools, techniques, and the specialized platforms — like Imagine.bo — that are turning months of “plumbing” into minutes of pure creation.
What Are AI-Powered Prompts in App Development?
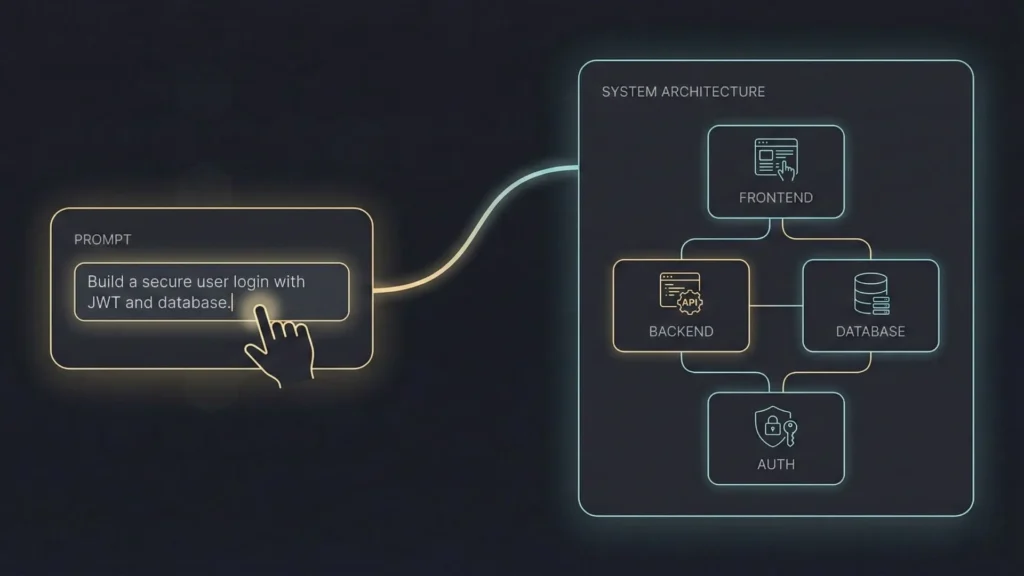
At its core, an AI-powered prompt is a natural language instruction given to a Large Language Model (LLM) to generate a specific, technical output. In the context of software development, this output isn’t just text — it’s functional code, UI/UX markup, database schemas, API integrations, and deployment configurations.
The Ultimate Pair Programmer
Think of AI as the ultimate partner. This partner has ingested nearly all of GitHub, Stack Overflow, and the world’s technical documentation. You aren’t just asking for a syntax reminder; you are collaborating with a system that understands architectural patterns. Many developers are already seeing the benefits of prompt-to-app development as it significantly reduces the barrier to entry for complex logic.
- A Simple Prompt: “How do I reverse a string in Python?”
- A Sophisticated Development Prompt: “Act as a senior backend developer. Generate a secure Node.js and Express endpoint using TypeScript. It needs to accept a JWT bearer token, validate it, and fetch user data from a PostgreSQL database. Include full try-catch blocks and error handling.”
The Spectrum of AI Tooling
The tools facilitating this workflow range in scope and abstraction:
- AI Chatbots (ChatGPT/Gemini): Your all-purpose problem solvers for brainstorming and debugging.
- IDE-Integrated Tools (GitHub Copilot): Real-time, context-aware suggestions that live inside your code editor.
- Specialized AI Platforms (Imagine.bo): These represent the highest level of abstraction. Instead of prompting for individual lines of code, you prompt for entire systems. These platforms understand business logic and generate SDE-level (Software Development Engineer) architectures from a single vision.
The Evolution of App Building: From Assembly to Conversational Abstraction
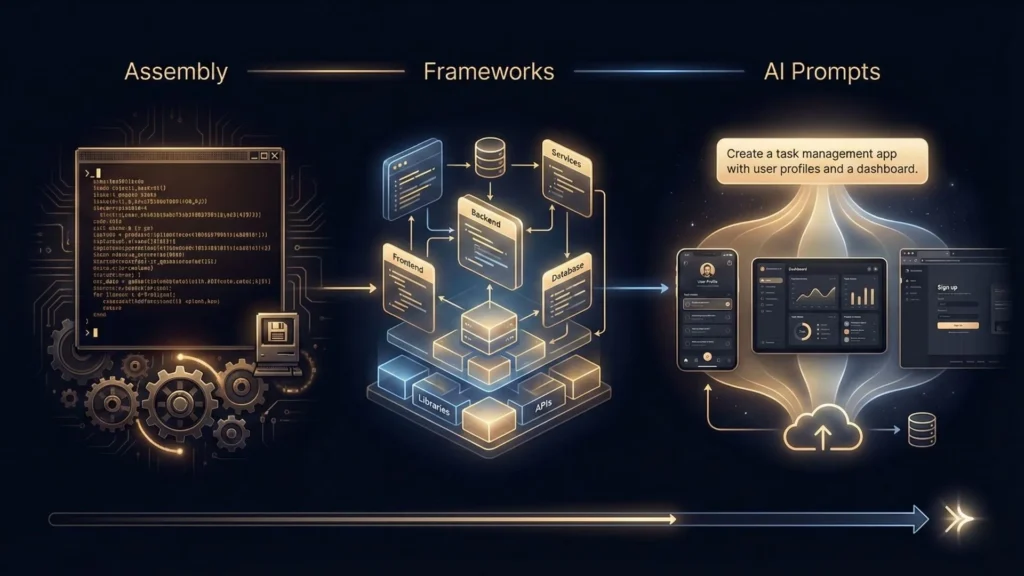
AI-powered development is the latest step in a long evolutionary process of abstraction. Each step has been designed to move the human further away from the “metal” and closer to the “idea.” Understanding the no-code vs traditional development debate is crucial here, as AI bridges the gap between these two worlds.
A Mini-Timeline of Development Abstraction
- 1950s (Manual & Assembly): Direct manipulation of machine code.
- 1980s (High-Level Languages): C and COBOL allowed logic to be written in a human-readable format.
- 2000s (Frameworks & Libraries): Ruby on Rails and Django allowed developers to assemble pre-built components.
- 2020s (Conversational Abstraction): We no longer drag “login blocks.” We describe the login flow we want.
Industry research by Gartner predicts that by 2028, 90% of enterprise software engineers will use AI code assistants. The evolution of developer roles is shifting from “coder” to “orchestrator.”
How AI Accelerates the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
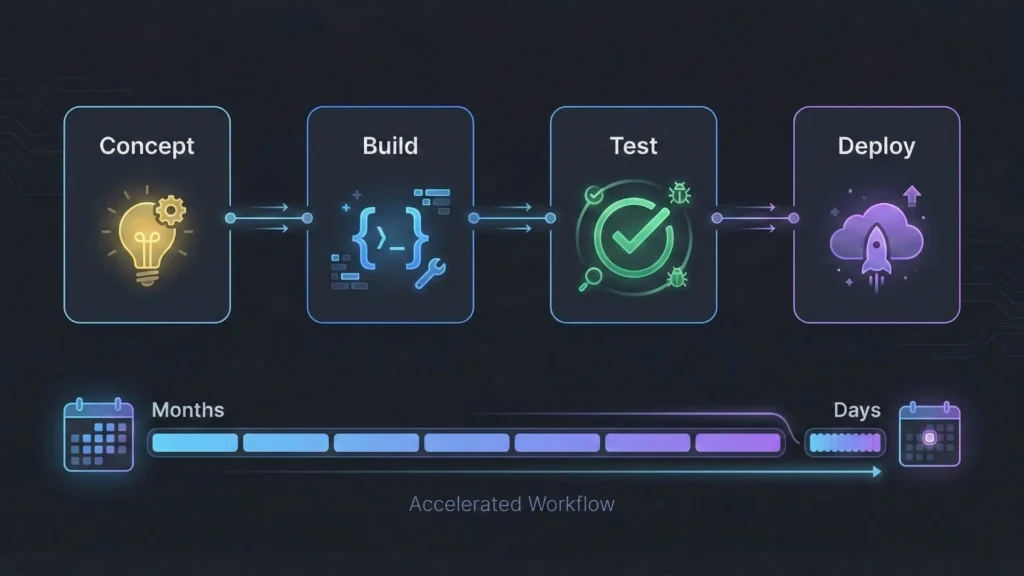
The true power of this paradigm is its ability to compress the SDLC. A process that once took months can now be prototyped in days. For those looking to validate an idea, following a guide to building a Minimum Viable Product with AI is the fastest route to market.
Step 1: Concept & Scaffolding (The “Describe” Phase)
Traditionally, this involved dense specification documents. Now, you use a Macro-Prompt.
- Prompt: “I’m building a personal finance tracker using the MERN stack. Generate the basic file structure, Mongoose schemas for transactions, and a basic Express server setup.”
Step 2: Component & Logic Generation (The “Build” Phase)
You work feature by feature.
- Frontend Prompt: “Create a React component for a transaction form using Tailwind CSS and react-hook-form. Include fields for date, amount, and category.”
- Backend Prompt: “Write the Express API endpoint to handle this form, including server-side validation and database persistence.”
Step 3: Deployment & DevOps (The “Launch” Phase)
- DevOps Prompt: “Write a multi-stage Dockerfile for this MERN application optimized for a cloud-native environment.”
Introducing Imagine.bo: The SDE-Level No-Code Revolution

While micro-prompting (writing code snippet by snippet) is powerful, it still requires the developer to manage the “plumbing” — the databases, the auth, the API routing, and the hosting.
This is where Imagine.bo enters the narrative. Learning how Imagine.bo works reveals a platform designed to execute the entire SDLC from a single high-level description, but with a critical difference: SDE-level engineering standards.
Why Imagine.bo is Different
Most no-code tools are “black boxes” that generate messy, unscalable code. Imagine.bo focuses on AI Reasoning. It doesn’t just automate; it thinks through the business logic.
- SDE-Level Architecture: Every app is built with clean, scalable, and secure code that follows industry best practices (clean architecture, SOLID principles).
- End-to-End Ownership: It handles the frontend, backend, databases, and deployment (AWS/GCP/Vercel) in one system.
- High Performance: Built to support up to 1,000 transactions per second, making it suitable for revenue-ready products, not just simple mockups.
For a developer, Imagine.bo handles the 80% of “boring” work (auth, CRUD, infrastructure), letting you focus on the 20% that makes your product unique.
Practical Prompting Techniques for Developers
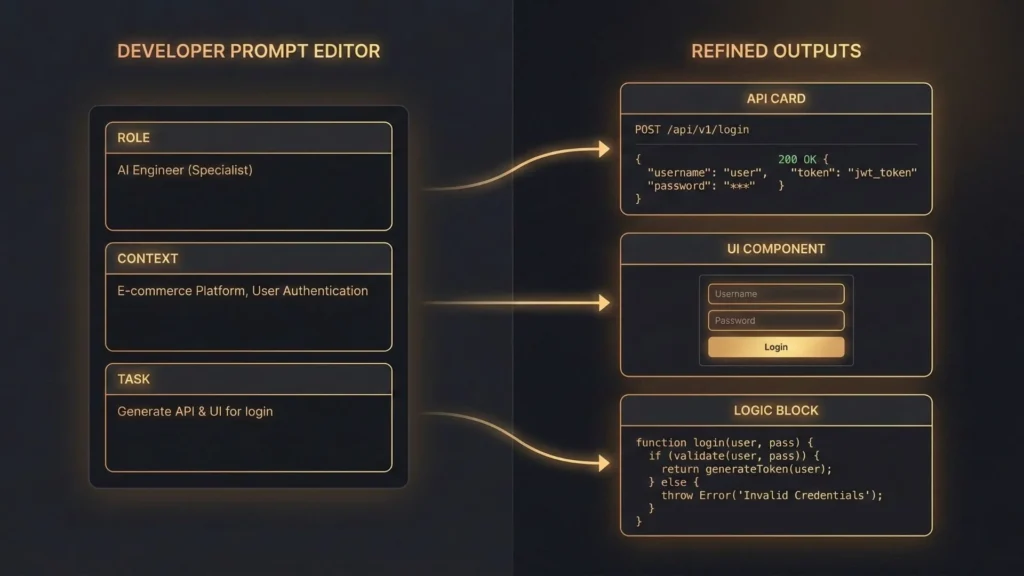
The quality of your output is 100% dependent on the quality of your prompt. Mastering specific prompt engineering tips can turn a mediocre output into production-grade code. Here are four frameworks to master.
1. The Role-Persona-Task (RPT) Framework
Give the AI a professional identity to ground its logic.
- Role: “You are an expert Senior Full-Stack Developer.”
- Persona: “You prioritize security, modularity, and clean documentation.”
- Task: “Generate a React hook for managing Google OAuth state.”
2. Few-Shot Prompting (Providing Context)
AI models are pattern-matchers. If you have an existing style guide, show it to the AI.
- Prompt: “Here is how we write our Button component: [Code]. Now, using this exact same style and prop-naming convention, create a Card component.”
3. Chain of Thought (CoT)
For complex algorithms, don’t ask for the answer immediately. Ask the AI to “think step-by-step.”
- Prompt: “Explain the logic for a custom recommendation algorithm first, then provide the TypeScript implementation.”
4. Macro-Prompting (The Imagine.bo Approach)
Instead of prompting for code, prompt for Business Outcomes.
- Prompt: “Build a mobile-first marketplace for local artists. It needs user profiles, a Stripe-powered checkout, and an admin dashboard to manage listings.”
Common Pitfalls and How to Navigate Them

AI is a powerful tool, but it is not infallible. Trusting it blindly is the fastest way to build buggy software.
Mistake 1: Blind Trust and Hallucinations
AI can confidently invent libraries or functions that don’t exist.
- The Fix: Treat AI code like a PR (Pull Request) from a junior developer. Review it, test it, and verify the libraries.
Mistake 2: Security Vulnerabilities
AI might suggest code that is functional but insecure (e.g., SQL injection or hardcoded keys).
- The Fix: Always apply security best practices for AI apps. Platforms like Imagine.bo mitigate this by using pre-vetted, enterprise-grade security protocols (GDPR/SOC2 ready) by default.
Mistake 3: Skill Atrophy
If the AI does all the thinking, your logic skills might weaken.
- The Fix: Use AI as a tutor. Ask it: “Why did you choose this specific sorting algorithm?” Use the generation as a starting point for deeper learning.
Case Study: The 72-Hour Side Project
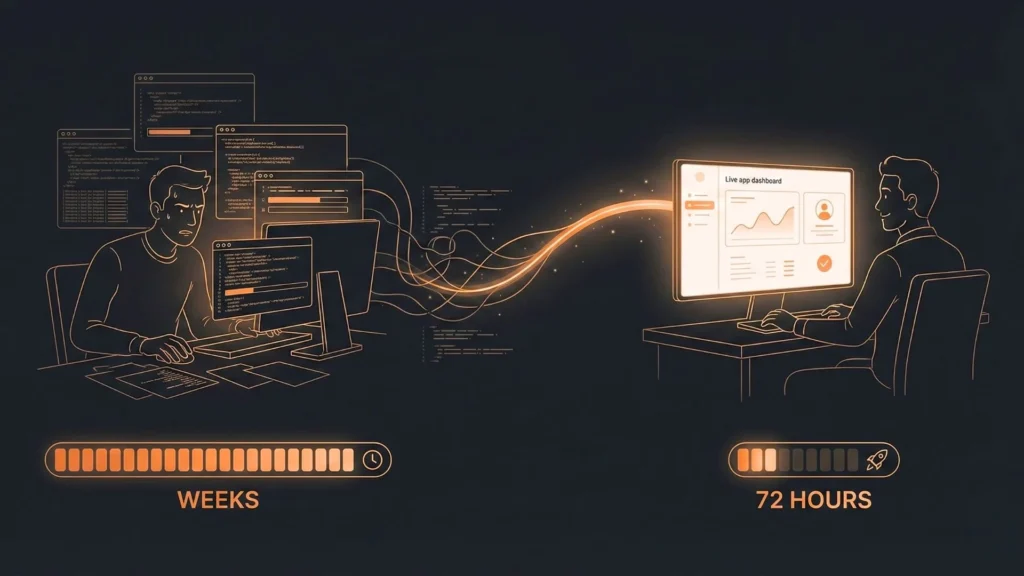
Let’s look at “Alex,” a developer with a great idea for a niche job board. Many founders use similar tools to launch your startup fast, and the results are often game-changing.
The Traditional Path (6 Weeks): Alex spends weeks wrestling with Passport.js for auth, setting up AWS buckets for resumes, and debugging CORS errors. By week 4, the excitement is gone, and the project is abandoned.
The AI-Orchestrated Path (1 Evening): Alex uses Imagine.bo.
- Vision: He describes the job board in plain English.
- Reasoning: The AI maps out the user roles (Employer/Seeker) and the database schema.
- Development: The system generates the full-stack app with SDE-level precision.
- Launch: One-click deployment to a live domain.
Alex spent his weekend marketing his app instead of debugging it. This is the shift from “implementer” to “founder.”
Conclusion: Your Future as a Developer-Orchestrator
The barrier between idea and execution has been demolished. We are no longer limited by how fast we can type, but by how clearly we can think. The future of app development belongs to those who can master the art of the prompt.
By automating the repetitive, time-consuming 80% of development, AI tools free us to focus on the delightful user experience and the unique business logic. Whether you are a senior engineer looking for a force multiplier or a founder looking for a technical co-founder, the tools are now in your hands.
Action Step: Don’t let your ideas stay in your head. Experience the transition from “Prompt to Prototype” today. Explore Imagine.bo to describe your vision and watch as AI builds a scalable, secure, and revenue-ready foundation in minutes. Once launched, don’t forget to implement robust SEO strategies for AI SaaS to ensure your product reaches its audience.
The tech stress of “How will I build this?” is over. The only question left is: “What will you build next?”
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





