Multi-tenant SaaS allows a single application instance to serve multiple customers, maximizing cost efficiency and scalability by sharing infrastructure while rigorously isolating data. This architecture simplifies maintenance and enables rapid growth without the overhead of dedicated servers for every client. By mastering key concepts like database partitioning, security compliance, and cloud deployment, founders can build flexible, profitable platforms. Whether using code or no-code tools, understanding multi-tenancy is the foundation for creating modern, scalable software solutions.
Understanding Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture
Multi-tenant SaaS allows a single application instance to serve multiple customers, maximizing cost efficiency and scalability by sharing infrastructure while rigorously isolating data. This architecture simplifies maintenance and enables rapid growth without the overhead of dedicated servers for every client. By mastering key concepts like database partitioning, security compliance, and cloud deployment, founders can build flexible, profitable platforms. Whether using code or no-code to AI code tools, understanding multi-tenancy is the foundation for creating modern, scalable software solutions.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildWhat Is Multi-Tenancy?
Multi-tenancy is a software architecture where a single application serves multiple customers, called tenants. Each tenant’s data and configurations remain separate, ensuring privacy and customization within the same application environment.
This architecture relies on shared infrastructure to reduce costs, improve resource utilization, and simplify maintenance. Tenants access the system through isolated logical partitions, which helps the platform maintain security and performance. For those new to the concept, understanding Multi-Tenant SaaS for Beginners is crucial for grasping how modern cloud applications operate efficiently.
Regulatory standards influence multi-tenant designs, requiring strict data isolation and auditability. Proper multi-tenant systems incorporate these standards to ensure compliance and protect sensitive information, particularly when navigating GDPR compliance in no-code environments.
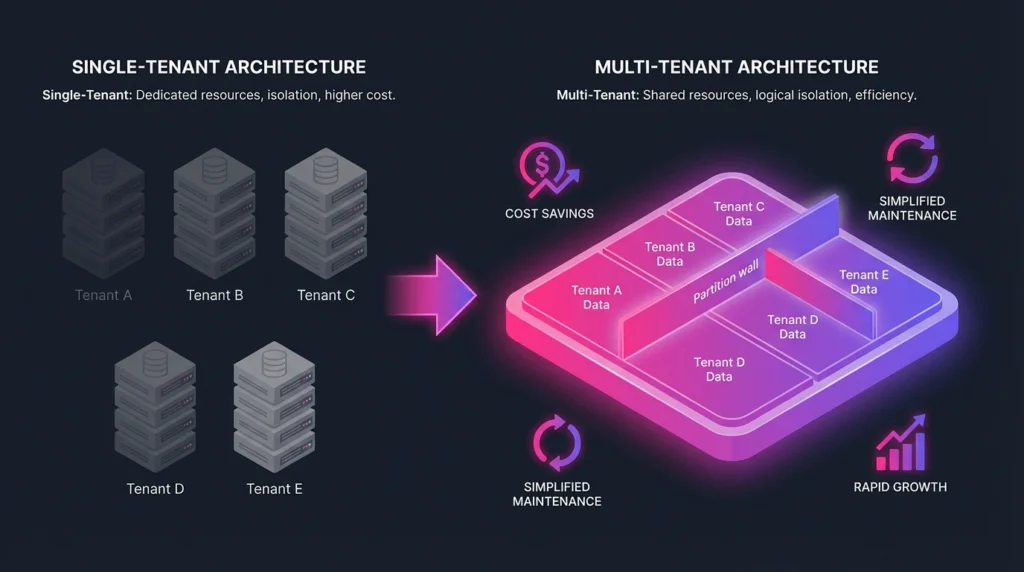
Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Models
In a single-tenant model, each customer has a dedicated application instance and infrastructure. This offers strong data isolation but demands higher operational costs and less efficient resource use.
Multi-tenant systems, on the other hand, run a single instance shared by multiple customers. This leads to scalable infrastructure benefits, as resources dynamically adjust to demand. Maintenance and upgrades are faster since changes apply centrally.
However, multi-tenancy requires careful design to prevent cross-tenant data access and maintain performance during peak usage. Businesses choosing between these models consider factors like security needs, customization, and budget constraints.
| Aspect | Single-Tenant | Multi-Tenant |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher due to dedicated servers | Lower due to shared resources |
| Maintenance | Individual updates | Centralized updates |
| Data Isolation | Strong | Logical separation required |
| Scalability | Limited by dedicated hardware | High, due to shared infrastructure |
Benefits of Multi-Tenant Platforms
Multi-tenant SaaS platforms offer cost efficiency by sharing hardware, reducing server maintenance, and optimizing resource use. This approach supports scaling SaaS with automation to accommodate growing customer bases without requiring new infrastructure for each tenant.
They facilitate consistent software updates and patching, ensuring all users benefit simultaneously, which reduces the operational burden. Built-in support for compliance frameworks like SOC 2 simplifies audits and enhances trustworthiness for enterprises concerned with security governance.
Customizable settings for individual tenants provide flexibility without sacrificing the advantages of shared infrastructure. This balance of scalability, security, and cost savings makes multi-tenancy a preferred option for SaaS providers targeting multiple customers.
Key Features of Multi-Tenant SaaS Solutions
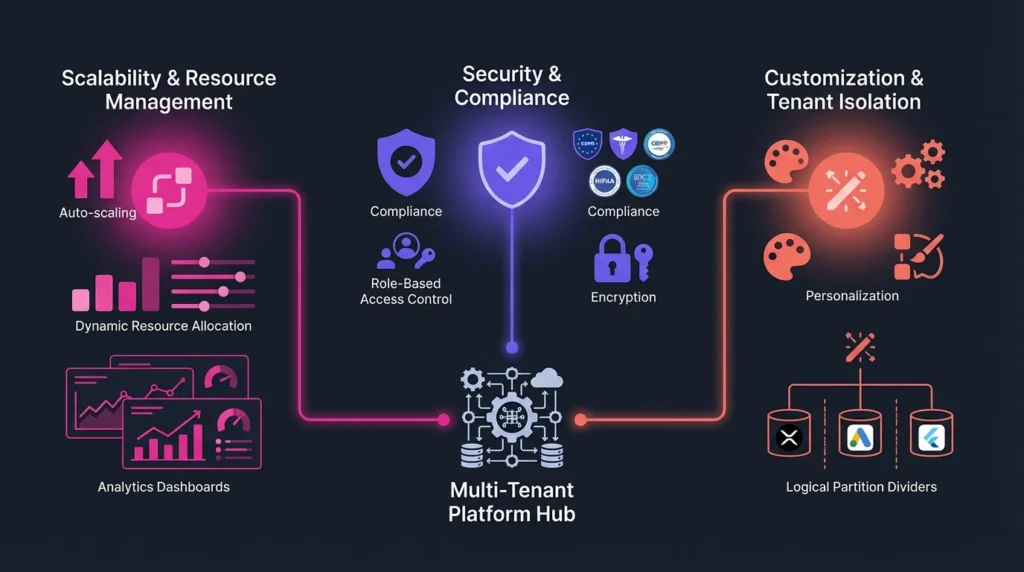
Multi-tenant SaaS solutions are designed to efficiently manage shared resources, protect data, and offer each user group specific configurations. These systems balance performance and security while allowing flexibility that meets diverse tenant needs.
Scalability and Resource Management
Multi-tenant SaaS relies on scalable infrastructure that dynamically adjusts to tenant demand. This ensures optimal resource allocation like CPU, memory, and storage among users without requiring separate hardware per tenant.
Efficient resource management reduces costs by consolidating workloads on shared servers. Automated scaling supports high traffic volumes and spikes, maintaining consistent application performance. Analytics dashboards often monitor resource use in real time, helping providers plan capacity and identify bottlenecks quickly.
Security and Compliance
Security checks and protocols are critical in multi-tenant environments to safeguard multiple customers on shared platforms. Strong tenant isolation prevents data leaks or unauthorized access across tenants. Best practices for securing web apps are essential in this architecture.
Compliance with industry standards and regulations requires regular audits and encryption at various layers. Providers implement role-based access controls, intrusion detection systems, and continuous monitoring. These measures ensure tenant data remains confidential and protected from vulnerabilities inherent to shared infrastructures.
Customization and Tenant Isolation
Even though tenants share the same software instance, each tenant can customize aspects like branding, workflows, and user roles. This preserves business-specific needs while leveraging pooled resources.
Tenant isolation plays a key role in customization by logically separating data and configuration settings. Techniques include schema-based or row-level data segregation in databases. This separation protects tenant data integrity and ensures that performance issues in one tenant do not affect others.
Choosing the Right Multi-Tenant SaaS Platform
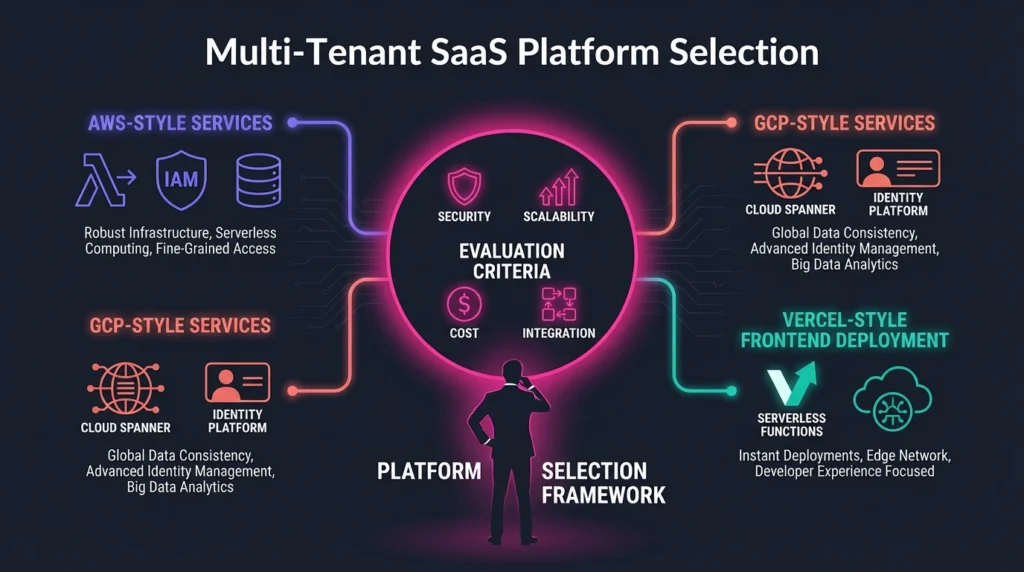
Selecting a multi-tenant SaaS platform requires careful analysis of the platform’s ability to meet business demands while ensuring security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Key aspects include infrastructure flexibility, data isolation, and integration capabilities. A robust Serverless SaaS architecture can often provide the necessary agility.
Essential Evaluation Criteria
- Security: This is paramount in multi-tenant environments where data from multiple clients coexists. Strong tenant isolation and compliance with standards such as GDPR or HIPAA should be confirmed.
- Scalability: Must be seamless to support growing user bases without performance drops. Look for platforms offering auto-scaling and load balancing features.
- Cost: Models vary; platforms like AWS and GCP provide pay-as-you-go pricing, allowing control over expenses. Assess whether pricing aligns with projected usage.
- Integration: Support for popular databases, authentication systems, and APIs can accelerate deployment.
Popular Platforms and Providers
- AWS: Offers a wide range of services suited for multi-tenant SaaS, including managed databases, IAM for tenant isolation, and robust autoscaling.
- GCP: Provides efficient multi-tenant support with tools like Cloud Spanner for global scaling and Identity Platform for secure authentication.
- Vercel: Focuses on front-end deployment and serverless functions, ideal for SaaS applications with dynamic web interfaces.
Getting Started With Imagine.bo

Imagine.bo offers a streamlined approach for building multi-tenant SaaS applications with a focus on practical tools and expert guidance. It provides an AI-generated blueprint that helps users design scalable architectures while also managing access through a controlled waitlist system. Learning how Imagine.bo works can be a game-changer for new founders.
How Imagine.bo Works
Imagine.bo guides users through designing multi-tenant SaaS platforms by generating a detailed architectural blueprint using AI. This blueprint outlines tenant isolation strategies, data partitioning, and resource allocation tailored to specific use cases.
The platform emphasizes scalability and security, ensuring tenants remain isolated while sharing infrastructure efficiently. Users can customize key components, such as identity management and consumption-based billing, directly through the interface.
Joining the Private Beta
Access to Imagine.bo currently requires joining a private beta. Interested users must register on the waitlist through the official website. The waitlist enforces a controlled roll-out, allowing Imagine.bo’s team to provide focused support and gather real-world feedback.
Available Support and Resources
Imagine.bo combines automated design tools with expert support to help users navigate multi-tenant challenges effectively. Users have access to an expert support team ready to troubleshoot architectural issues and provide best practice advice.
Zero-Code Development for Beginners

Zero-code development allows individuals to create complex SaaS applications without writing any code. Users can focus on describing their ideas clearly while tools handle the technical implementation. This approach often offers one-click build options to build apps with AI quickly.
Introduction to No-Code Platforms
No-code platforms provide ready-made components and visual interfaces for building software. Users arrange features through drag-and-drop editors instead of coding. These platforms include templates for user authentication, billing, and multi-tenant data segregation, which are essential in SaaS applications.
Building Apps Without Programming
Building apps without programming entails selecting tools that translate user designs into running software automatically. It is now possible to build an app for free with AI, enabling immediate deployment after configuration. Essential SaaS capabilities such as subscription management, user roles, and data isolation per tenant are often pre-built.
Benefits for Solo Founders and Agencies
Solo founders and agencies benefit greatly from zero-code development by reducing dependency on technical teams. This era of solo entrepreneurship with generative AI allows for rapid prototyping and iteration on SaaS products based on direct feedback, speeding up validation and market entry.
Scaling and Managing Your Multi-Tenant SaaS Product
Effective scaling and management ensure a multi-tenant SaaS handles increasing user demands while maintaining performance and cost efficiency.
Traffic Handling and Performance
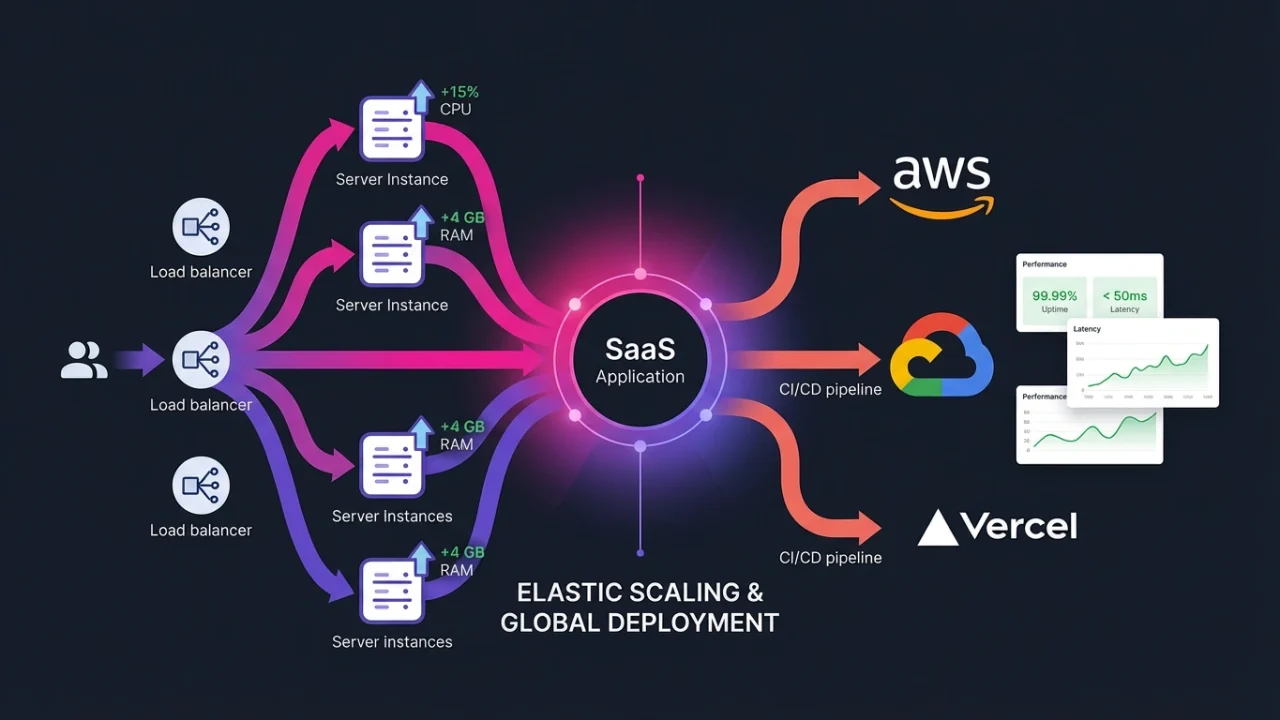
Managing traffic in a multi-tenant SaaS requires load balancing and traffic distribution to avoid bottlenecks. Using elastic load balancers with auto-scaling groups on AWS or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) allows the system to dynamically allocate resources based on user demand.
Deploying to Cloud Environments
Deploying a multi-tenant SaaS product on cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, or Vercel enables flexible and scalable infrastructure management. These providers offer managed services that simplify CI/CD pipelines, automated scaling, and disaster recovery.
Pricing Models and Cost Management
Effective pricing and managing costs are crucial for a multi-tenant SaaS to scale profitably. Clear pricing structures help you monetize AI SaaS tools effectively.
Understanding Subscription Models
Subscription pricing is the most common approach in multi-tenant SaaS, where customers pay a recurring fee—monthly or yearly—for access.
- Flat-rate pricing: A fixed fee for all users.
- Tiered pricing: Different levels of service at increasing price points.
- Usage-based pricing: Charges based on actual consumption.
Cost Optimization Tips
Cost efficiency in multi-tenant SaaS involves balancing shared infrastructure benefits with tenant isolation needs. Key strategies include choosing the right database model, utilizing autoscaling to match resources with demand, and regular monitoring of usage patterns.
Expert Support and Community Resources
Access to specialized technical help and peer knowledge are essential when building and maintaining a multi-tenant SaaS platform.
Accessing Engineering Help
Many SaaS teams rely on expert backup from senior engineers to navigate complex issues in multi-tenant architecture. These professionals provide guidance on topics such as database design, tenant isolation, and scalability challenges.
Learning From Community Practices
Active participation in developer forums, open-source projects, and industry webinars provides valuable insights into multi-tenant SaaS challenges. Communities such as GitHub, Reddit, and vendor-specific forums allow developers to share real-world experiences and solutions.
Key community resources include:
| Resource | Focus Area | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| AWS SaaS Architecture | Cloud scalability and cost | Expert-led sessions and documentation |
| Reddit /r/dotnet | SaaS app development | Peer advice and code reviews |
| Dev Community Blogs | Multi-tenant design patterns | Tutorials and best practices |
Leveraging these resources supports continuous learning and innovation in multi-tenant SaaS development.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build