For the modern founder, the path from a napkin sketch to a market-ready product has never been shorter. By the end of 2025, an estimated 70% of new applications will be built using no-code or low-code platforms, signaling a fundamental shift in how software is conceived and delivered. However, as many product leaders have discovered, there is a vast gulf between launching a functional MVP and maintaining a scalable SaaS architecture that can withstand the pressures of rapid user growth, complex data security, and enterprise-grade performance.
Traditional no-code tools often prioritize speed over structural integrity, leading to a “technical ceiling” where the platform becomes unstable as it reaches thousands of users. To build a business that lasts, founders must look beyond simple drag-and-drop interfaces toward robust and flexible solutions powered by SDE-level (Software Development Engineer) architecture.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildDefining Scalable SaaS Architecture for the Business Leader
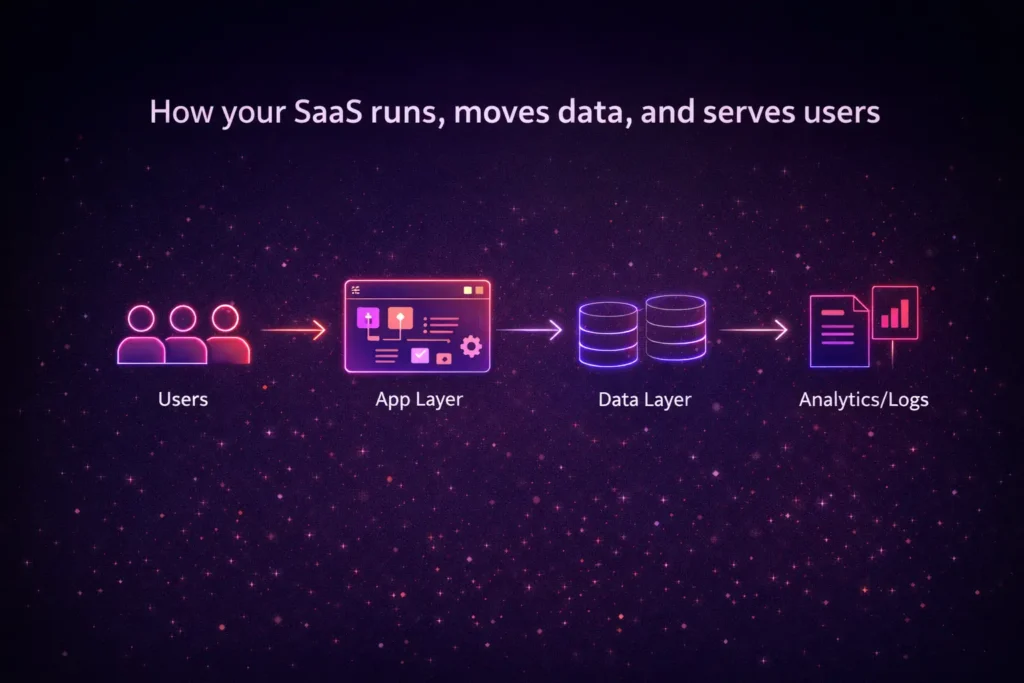
In its simplest terms, SaaS architecture is the structural design that defines how your code runs, how your data flows, and how your users access your service. For a founder, a well-designed architecture is not just a technical requirement; it is a business advantage that ensures your success does not become a technical liability.
A truly scalable architecture provides three critical benefits:
- Predictable Economics: Your infrastructure costs should grow proportionally with your revenue, rather than spiking unpredictably.
- Automatic Growth Handling: The system should handle a jump from 100 to 100,000 users without requiring a total rebuild.
- Operational Reliability: High availability through distributed systems ensures your platform remains online even if specific components fail.
While early-stage startups often start with a monolithic architecture (a single, unified codebase) for speed, long-term scalability usually requires transitioning to microservices, where the application is broken into independent, modular components that communicate with each other.
The Pillars of a Robust SaaS Solution

To outperform the competition, your platform must be built on a foundation of “SDE-level” principles. These are the core standards that separate professional SaaS products from simple internal tools:
A. Multi-Tenancy and Data Isolation
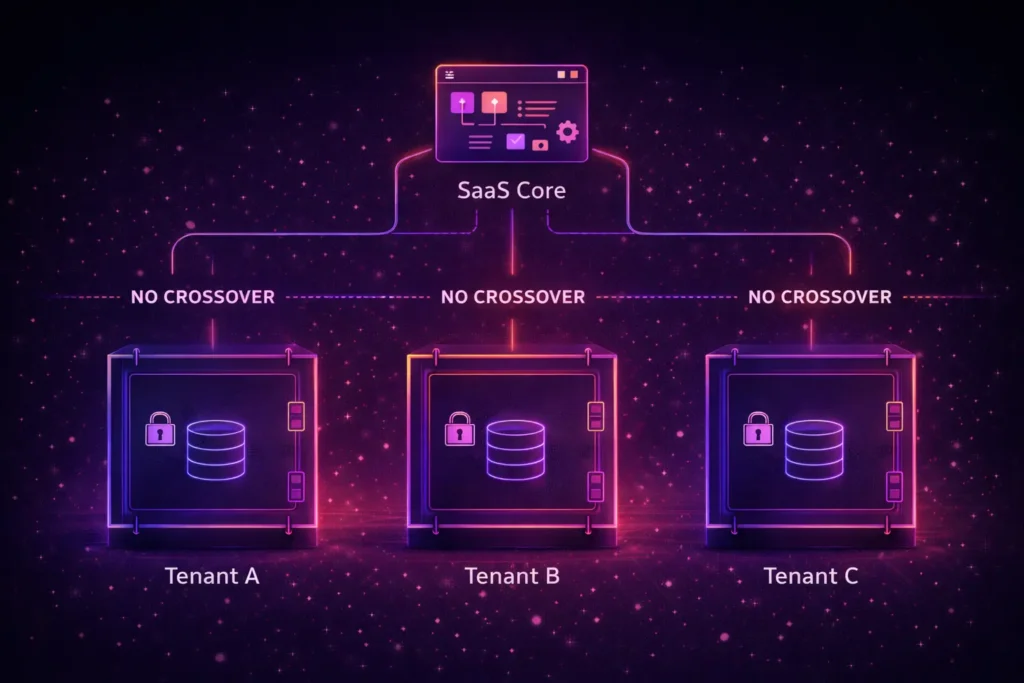
Most modern SaaS platforms utilize multi-tenant architecture, where a single application instance serves multiple customers. This “one-to-many” model is highly efficient and simplifies updates across your entire user base. However, robustness depends on how strictly you isolate tenant data. You must ensure that even though users share the same infrastructure, their data and configurations remain completely private.
B. High Performance and Low Latency
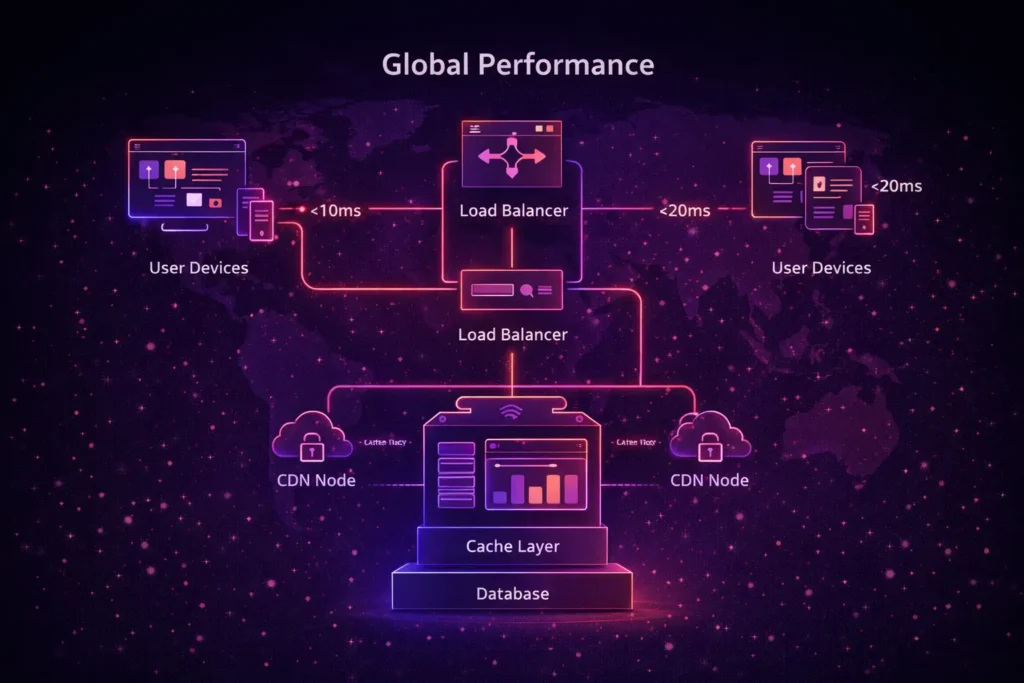
Performance is about delivering a responsive user experience regardless of the user’s location. This is achieved through:
- Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single point of failure.
- Caching: Storing frequently used data in “high-speed” layers to reduce the time spent fetching information from slow databases.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Speeding up asset delivery by hosting files on servers closer to the end-user.
C. Enterprise-Grade Security
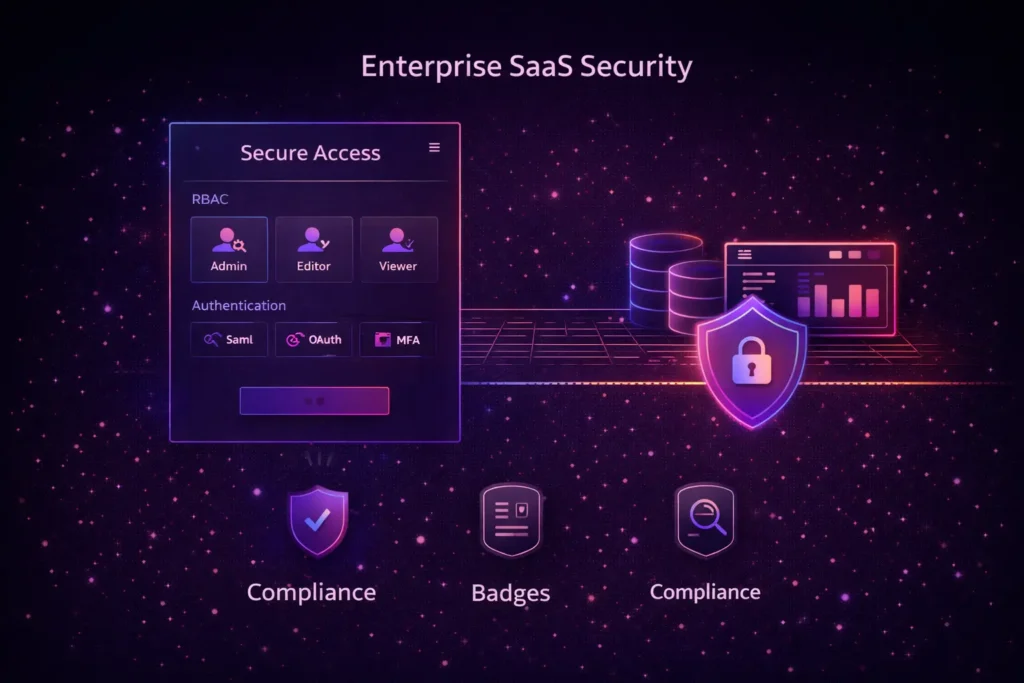
Security cannot be an afterthought. A robust solution must include encryption at rest and in transit, strict Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and compliance with global standards like GDPR or SOC 2. By building these into the architecture from day one, you avoid costly retrofits and build immediate trust with enterprise clients.
AI-Driven Architecture vs. Traditional Drag-and-Drop
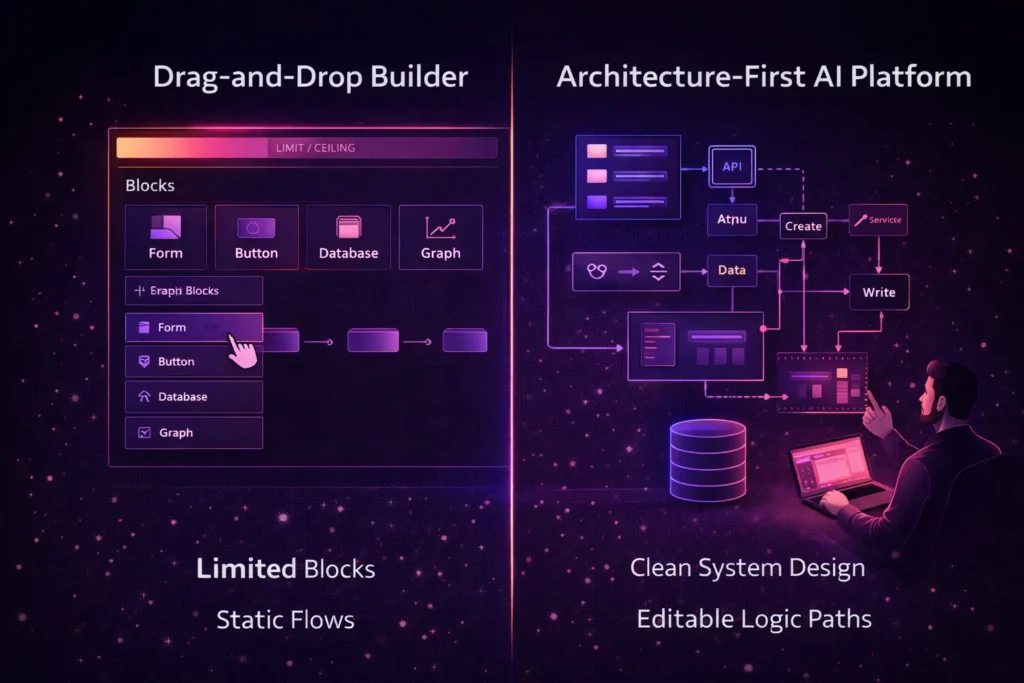
The no-code landscape is currently split into two camps: traditional visual builders and AI-powered visual development platforms like Imagine.bo.
Traditional no-code tools (like Webflow or Adalo) are excellent for specific use cases but often involve trade-offs between ease of use and deep customization. They typically operate like “LEGO blocks”—you are limited by the pre-built components in the library. If your product needs a feature the library doesn’t support, you often hit a “wall”.
AI-driven, SDE-level platforms represent the next generation. Unlike “vibe-coding” (where AI generates a “black box” of code that you can’t read or fix), an architecture-first platform like Imagine.bo uses an AI reasoning engine to generate clean, professional-grade architecture.
The difference is critical:
- Control: In traditional AI coding, you may get 80% of the way there in minutes, but the final 20% involving complex bugs or privacy settings can leave you stuck in endless “prompt loops”.
- Maintainability: AI-driven platforms like Imagine.bo provide a visual programming language that allows you to see and edit the logic directly, ensuring you aren’t reliant on an AI that might “forget” your codebase as it grows.
Overcoming the Real-World Challenges of Scaling
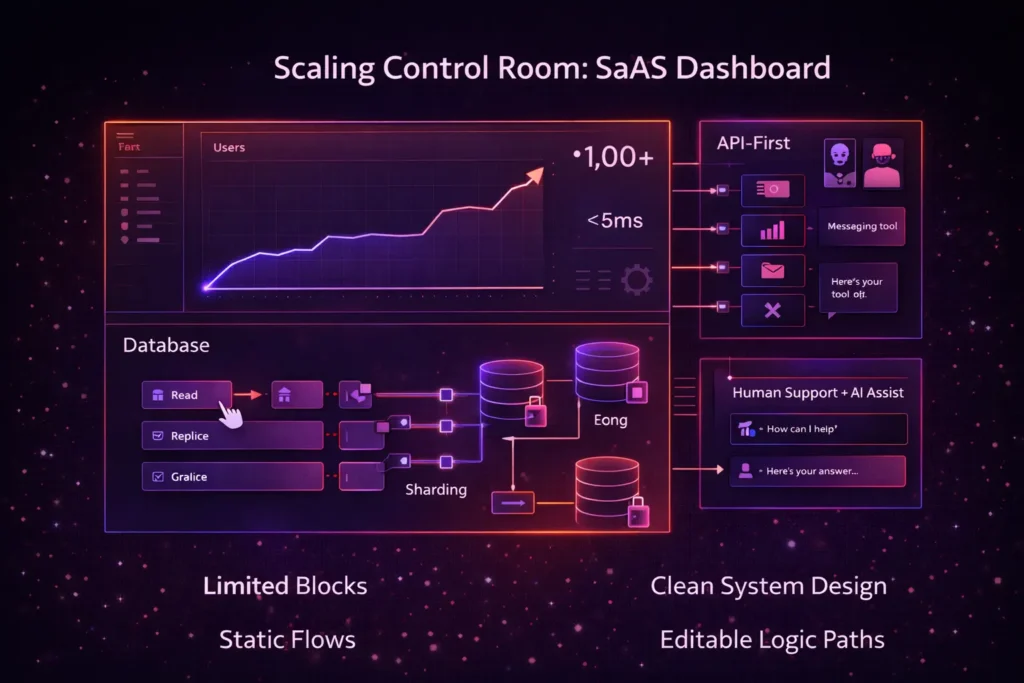
Scaling a SaaS isn’t just about adding more servers; it’s about managing complexity. Founders often face specific technical bottlenecks once they cross the 1,000-user threshold.
The Database Bottleneck
As your data grows, standard databases can slow down. Robust solutions utilize database replication (creating copies of the database to share the load) or sharding (splitting data across different servers) to keep queries fast.
Extensibility and the “Vendor Lock-In” Trap
Many founders fear “vendor lock-in”—the inability to move their product if a platform changes its pricing or features. To ensure long-term flexibility, look for platforms that support API-first development and use standard data formats. This allows you to connect your SaaS with thousands of other tools or even migrate your logic if necessary.
The Need for Human + AI Support
No matter how powerful the AI, complex business logic sometimes requires human intuition. The most successful no-code journeys are those supported by continuous support systems that combine AI-speed with human expertise.
Why Imagine.bo Defines the Future of No-Code

Imagine.bo is designed for founders who refuse to settle for “prototype-grade” software. It moves beyond the limitations of traditional drag-and-drop by focusing on architecture-first development.
Key Strengths of the Imagine.bo Approach:
- AI Reasoning Engine: Instead of just generating snippets of code, our AI understands the underlying intent of your business logic, creating a structured, SDE-level foundation that is both readable and scalable.
- Cloud-Native Deployment: Leveraging industry leaders like AWS, Imagine.bo ensures your application is built on a cloud-native infrastructure that supports horizontal scaling, automated failovers, and global delivery.
- End-to-End Ownership: You maintain full control over your data, design, and logic, avoiding the “black box” limitations of typical AI generators.
- Enterprise Security from Day One: With built-in encryption, user authentication (including 2FA), and rigorous compliance standards, your application is ready for the most demanding corporate environments.
- Continuous Human + AI Support: We bridge the gap between AI efficiency and human strategy, providing the resources you need to solve complex architectural challenges.
Architectural Thinking: A Founder’s Checklist
Before committing to a platform for your SaaS, ask these four architectural questions:
- Can I scale parts of the app independently? (Microservices vs. Monolith).
- Is the security infrastructure built-in or bolted-on?.
- Does the platform handle “stateless” APIs for easier horizontal scaling?.
- Can I customize the “final 20%” of my product without getting stuck in a prompt loop?.
Conclusion: The Architecture-First Revolution
The era of “just build it fast” is evolving into the era of “build it right, fast.” For a founder, the goal is to create a product that can grow from a simple MVP into a global enterprise solution without the need for a traumatic re-engineering project.
By choosing an architecture-first no-code platform like Imagine.bo, you aren’t just building an app; you are engineering a robust, flexible, and scalable digital asset. The future of SaaS belongs to those who understand that while the interface may be “no-code,” the foundation must always be “pro-grade.”
Analogy for Understanding: Think of building a SaaS like building a skyscraper. Traditional no-code is like using high-quality pre-fabricated rooms—great for building a two-story house quickly, but impossible to stack 50 stories high. Imagine.bo is like having an AI-powered master architect and a crew of expert engineers: it provides the structural steel and deep foundations (the SDE-level architecture) first, so you can keep building higher and higher without the whole thing leaning or cracking under the weight of your success
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build