The landscape of software development is undergoing a seismic shift. We have moved from the era of manual syntax to the era of visual logic, and now, we are entering the era of natural language intent.
For the no-code developer, this is a superpower. You no longer need to manage complex infrastructure or write deep-learning algorithms to build sophisticated, AI-driven products. However, as the technical barriers fall, a new challenge emerges: communication. The quality of your AI product is now directly tethered to the quality of your instructions.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildThis is Prompt Engineering. It’s not just “chatting with a bot”; it’s the bridge between a visionary idea and a production-ready application. This guide will walk you through the nuances of mastering this bridge, ensuring your no-code projects are predictable, scalable, and genuinely powerful. If you are just starting, you can build your own AI app guide to see these principles in action.
Defining Prompt Engineering in the No-Code Ecosystem
In a traditional coding environment, logic is rigid. If $x$, then $y$. In the no-code AI world, logic is fluid. Prompt engineering is the process of structuring fluid language into a format that a Large Language Model (LLM) can treat as a set of instructions.
Beyond “Clever Sentences”
A common mistake is treating prompt engineering like a creative writing exercise. While clarity is vital, professional prompt engineering is about architecture. You aren’t just asking for a favor; you are designing a system.
In a no-code platform, prompts often live inside “blocks” or “nodes.” They interact with:
- Visual Controls: Sliders for “temperature” (creativity) or “top-p” (diversity).
- Data Inputs: Variables pulled from a user’s database or a form submission.
- Workflow Logic: If the AI returns a specific keyword, the no-code tool triggers a secondary action.
To understand how these pieces fit together, check out this no-code vs traditional development breakdown.
The “Intent Gap”
Human communication relies heavily on subtext. AI does not. If you tell a human, “I need a headline for my site,” they might look at your brand colors and target demographic to infer a style. An AI will simply give you a headline.
Effective prompts bridge this Intent Gap by explicitly defining the role, task, context, and constraints. This level of precision is essential when you build an app by describing it, as the AI needs a clear roadmap to generate functional components. If you have a concept ready to test, you can start building your app for free to see how the platform translates your intent into architecture.
The Core Pillars: Context and Specificity

If you take only one lesson from this guide, let it be this: The more the AI knows about the “Why” and the “Who,” the better the “What” will be. ### The Power of Context
Context provides the “guardrails” for AI reasoning. Without it, the model defaults to the most generic average of its training data. When prompts lack context, outputs tend to be generic or misaligned.
Compare these two requests:
- “Summarize this article.”
- “Summarize this article in three bullet points, focusing on key insights for startup founders.”
The second prompt clearly defines audience, format, and purpose. That extra structure dramatically improves usefulness. By narrowing the focus, you increase the density of value in the output.
Specificity in Action
Specificity is about replacing abstract adjectives with concrete parameters. Instead of “make it look professional,” use “maintain a minimalist, corporate aesthetic with a focus on high-readability sans-serif typography.”
Specific language also plays a role in image generation and UI design. Instead of saying “make an image,” saying “generate a clean, modern product dashboard UI with neutral colors and clear typography” sets expectations the model can follow. Mastering this skill is a prerequisite for anyone looking to monetize prompt built apps no code style, as high-quality output is what users are willing to pay for.
A Taxonomy of Prompts for Builders
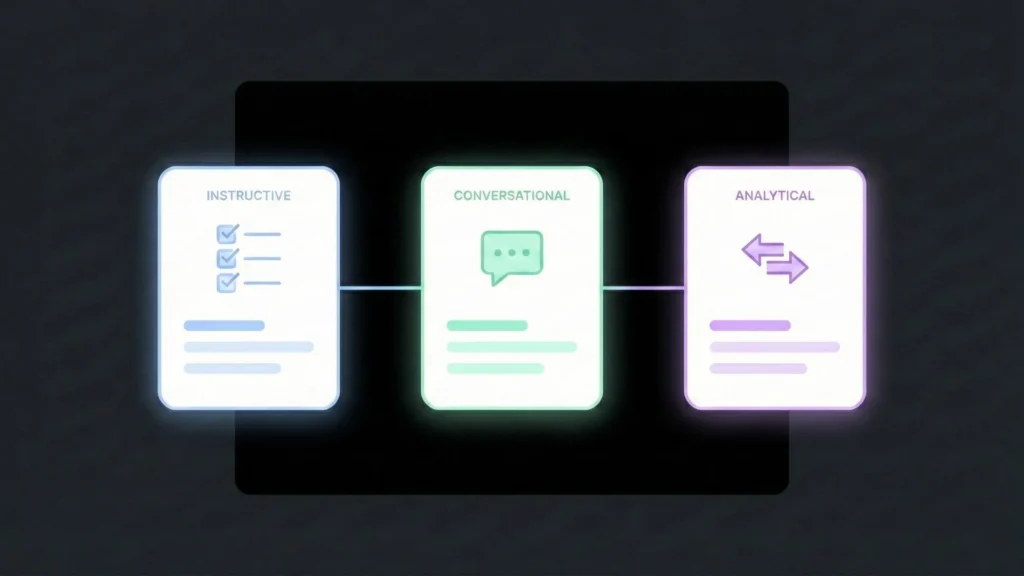
Not all prompts serve the same purpose. Depending on where you are in your no-code build, you will alternate between these primary archetypes:
I. Instructive Prompts (The “Workhorse”)
Instructive prompts are direct and task-focused. They work best when you need structured output. They are the backbone of automated workflows summarizing tickets, generating reports, or transforming data formats.
- Example: “Generate a 500-word comparison of no-code and traditional development, focusing on speed, cost, and scalability.”
II. Conversational Prompts (The “Architect”)
Conversational prompts are more open-ended and exploratory. They encourage brainstorming and creative thinking. You aren’t looking for a finished product yet; you’re looking for a partner to explore the problem space. This is a common strategy used by non-technical founders building products to validate their logic before going live.
- Example: “Let’s brainstorm feature ideas for a productivity app aimed at remote teams.”
III. Structural & Comparative Prompts (The “Analyst”)
Other prompt types include comparative prompts for side-by-side analysis and question-and-answer prompts for factual responses. These prompts help you make decisions. You can feed the AI two different ideas or datasets and ask for a trade-off analysis.
- Example: “Compare the user onboarding flow of App A and App B. Identify which one is more likely to reduce churn for non-technical users and explain why.”
Advanced Techniques: Moving Beyond One-Liners
To build truly “smart” no-code applications, you need to employ techniques that go beyond simple instruction.
Few-Shot Learning (The “Show, Don’t Tell” Method)
LLMs are incredible pattern matchers. Instead of explaining a complex format, show the AI three examples of what you want. This is called “Few-Shot” prompting. It includes example input-output pairs inside the prompt itself to help the model understand the task more precisely.
For classification, formatting, or structured generation, three to five examples often deliver the best balance between clarity and flexibility.
Prompt Chaining (The “Modular” Workflow)
In no-code development, we rarely build one giant function. We build small, interconnected steps. Prompt engineering should follow the same logic. Prompt Chaining breaks complex workflows into smaller steps, where each output feeds into the next prompt.
- Step 1: Generate target user personas.
- Step 2: Create messaging tailored to each persona.
- Step 3: Refine copy for clarity and tone.
This approach offers more control and aligns well with visual no-code workflows. This modularity is key when you want to build complex apps with imaginebo, allowing for nuanced logic and reliable performance.
Writing Better Prompts for No-Code AI Platforms
The best prompts are concise and intentional. Overloading a single prompt with too many requirements often reduces output quality.
Keep Prompts Clear and Focused
Start with the core task. If you need more detail, refine through follow-up prompts rather than one long instruction. This mirrors how no-code systems are designed to work: small, modular steps instead of monolithic logic. Clean formatting and clear examples lead to cleaner output.
Refine Through Iteration
Prompt engineering is not a one-shot process. Test, evaluate, and adjust. Small changes in wording can lead to large improvements. Ask yourself:
- Is the output accurate?
- Does it match the intended tone?
- Is it usable without heavy editing?
Integrating AI with No-Code Platforms
The real magic happens when your prompts interact with a platform’s native features. Modern tools are evolving from simple “wrappers” to “reasoning engines.” Modern no-code platforms increasingly combine prompt engineering with full product generation. Instead of stitching together multiple tools, founders can move from idea to launch in a single environment.
The Rise of Generative Products

Platforms like Imagine.bo represent the next frontier. They don’t just “help you write”; they help you architect. Instead of you manually building every database table and API connection, you describe the business logic in plain English. Rather than focusing only on automation, Imagine.bo treats prompts as product inputs.
The system uses that prompt to:
- Reason through the necessary user roles.
- Generate the database schema.
- Build the frontend UI components.
- Ensure the output is scalable, secure, and production-ready.
In this context, the prompt isn’t just a command; it’s a Product Requirement Document (PRD) that the platform executes. For more on this, explore the ai powered no code app development ecosystem.
Practical Use Cases for Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering plays a role across many no-code applications:
- AI Chatbots: Delivering consistent, contextual responses for customer service.
- Marketing Content: Tailoring copy to specific audiences and channels.
- Automated Data Analysis: Generating reports and insights from raw data.
- Rapid MVP Creation: Allowing founders to test new ideas in days instead of months.
When prompts are structured correctly, these systems become reliable partners rather than unpredictable tools.
Common Challenges and How to Handle Them
Even with the best intentions, prompts can fail. Understanding why is the first step toward a fix.
Unclear or Generic Outputs
When results feel vague, the issue is usually the prompt. Add context, clarify the audience, or specify the format. Avoid assuming the AI understands unstated intent.
Bias in AI Responses
AI reflects the data it was trained on. Monitor outputs carefully and adjust prompts to encourage balanced perspectives. Regular review is essential, especially in user-facing products.
Debugging Prompt Issues
Track prompt versions and results. Treat successful prompts as reusable assets. Over time, this becomes a powerful internal knowledge base. If you are struggling with logic errors, creative debugging for no code builders offers great strategies to get your project back on track.
The Future of No-Code AI and Prompt Engineering
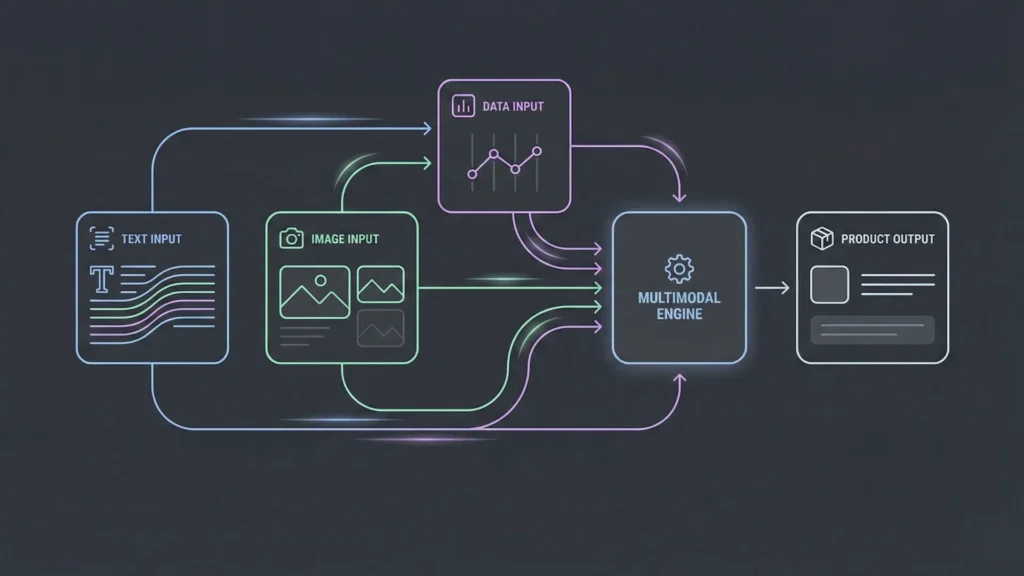
Prompt engineering is becoming a core skill for modern builders. As no-code platforms integrate deeper AI reasoning, the ability to express intent clearly will matter more than technical syntax.
We are already seeing a shift toward:
- Multimodal Prompts: Using text, images, and data simultaneously.
- Structured Workflows: Moving from isolated tasks to end-to-end business goals.
- AI Orchestration: Systems that manage the entire product lifecycle from idea to deployment.
This evolution is lowering the barrier to entry even further, enabling single person startups using ai to compete with much larger organizations. For founders and creators, this means fewer tools, faster launches, and more focus on outcomes instead of implementation details.
Final Thoughts
Prompt engineering is not about tricking AI into better answers. It is about learning how to think clearly, define intent, and communicate requirements precisely. For no-code developers, this skill unlocks a new level of control.
When paired with platforms that handle engineering, security, and deployment behind the scenes, prompts become the bridge between vision and execution. Master that bridge, and building powerful AI products becomes less about code and more about clarity.
If you’re ready to turn your ideas into a functional reality, you can launch your AI application now and experience the power of prompt-to-product development. For more strategic advice, see how you can launch your idea guide today.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





