The idea of the smart home has shifted from a futuristic daydream to something we actually live with every day. A decade ago, talking to a computer seemed impossible; now, Smart Home Voice Assistants have quietly replaced keyboards for a lot of our daily tasks. However, buying a smart speaker doesn’t automatically give you a smart home. There is still a significant gap between having a few cool gadgets and creating a living space that truly understands and adapts to you.
Most homeowners find themselves trapped between two extremes: basic, limited consumer ecosystems like Alexa or Google Home, or highly complex, code-heavy DIY projects using Python and obscure APIs. This guide bridges that gap. We will explore how to build your dream smart home using a no-code voice assistant DIY guide that focuses on professional-grade architecture, sophisticated AI reasoning, and robust security all without writing a single line of code.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildThis guide will illustrate how to successfully integrate a Smart Home Voice Assistant into your living space, enhancing convenience and smart functionality.
Understanding the Architecture of an Intelligent Home

To build a high-authority smart home system, one must understand that it is more than just a collection of Wi-Fi light bulbs. A true smart home is an ecosystem where connected devices manage lighting, climate, security, and more through a central system. For a deeper dive into how these devices communicate, you can read our expert guide on combining IoT and AI in no-code projects.
The Three Levels of Automation
A comprehensive smart home functions on three distinct levels:
- Basic Control: Manual intervention via apps or voice commands to trigger a single action.
- Scheduled Automation: Routines based on time or simple triggers (e.g., turning on porch lights at sunset).
- Full Integration: Multiple devices working across the home automatically, driven by context and reasoning.
The Technical Foundation: Protocols and Connectivity
The “backbone” of your smart home is the network protocol used for communication.
- Wi-Fi: The most common protocol due to ease of use, though it can crowd home networks if too many devices are added.
- Zigbee and Z-Wave: Mesh protocols that consume less power and allow devices to talk to each other over long distances without clogging Wi-Fi.
- Matter: An emerging standard designed to ensure cross-brand compatibility.
While many DIY guides focus on simple Wi-Fi setups, Imagine.bo leverages SDE-level (Software Development Engineer) architecture to manage these protocols at scale. This allows users to build systems that handle hundreds of devices across complex mesh networks without the latency issues common in basic consumer hubs.
The No-Code Voice Assistant DIY Guide: From Script to Reasoning
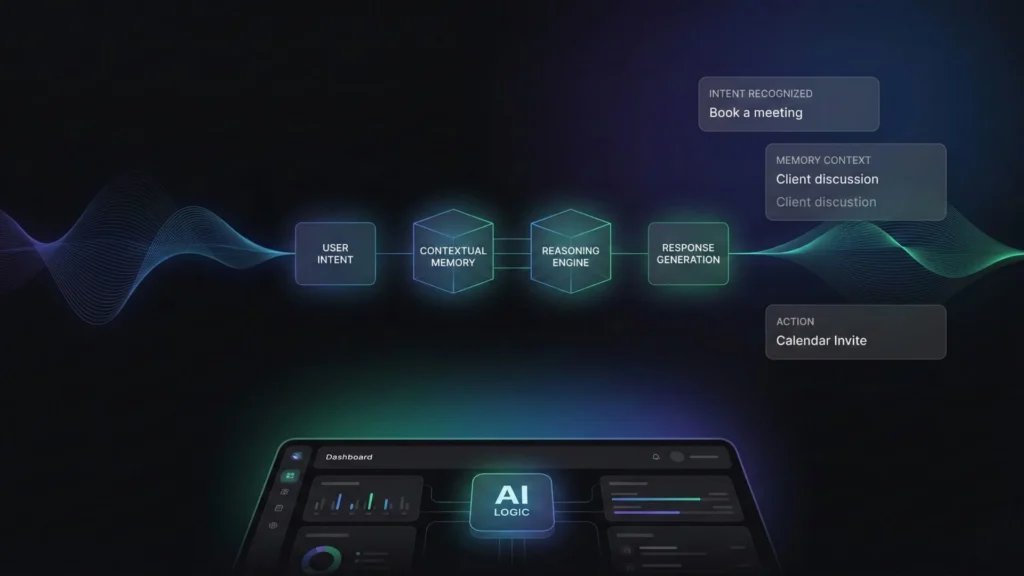
Most “DIY” voice assistant guides require you to install Python libraries like pyttsx3 or speech_recognition and write hundreds of lines of code to perform simple tasks like checking the weather. While this is a great learning exercise, it is not scalable for a modern home.
The Evolution of Voice Interfaces
A voice assistant consists of three core components:
- Speech-to-Text (STT): Converting your verbal command into a text script.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Analyzing the intent behind the words.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): Generating a spoken response.
Traditional assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant are often “command-based” they look for specific catchphrases. If you don’t say the exact phrase, they fail. Modern AI assistants, however, use Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand the intent behind the words. If you want to customize how your assistant speaks and interacts, check out our guide on how to build your own AI voice app.
Building Custom Logic with Imagine.bo

Imagine.bo replaces traditional Python scripting with AI reasoning. Instead of hard-coding every possible command, you use a no-code interface to define the “world” of your home. You can assign a personality to your assistant and give it access to your home’s “context”. This allows for context sharing, where the assistant remembers previous commands to handle follow-up requests naturally.
Step-by-Step: Building Your Dream Smart Home

Step 1: Establish a Robust Network
Your smart home is only as strong as its Wi-Fi. In larger homes, mesh systems or Wi-Fi extenders are necessary to eliminate dead zones.
- Pro Tip: For high-bandwidth devices like security cameras, ensure there is a strong signal at the exact mounting location.
- Security Note: Always use WPA3 encryption and consider a separate Wi-Fi network for your IoT devices to isolate them from your personal data. For more on keeping your system safe, review our no-code app security best practices.
Step 2: Choose Your Foundational Hardware
Begin with high-impact, easy-to-install devices:
- Smart Hub: The “brain” that allows you to control everything from one dashboard.
- Smart Lighting: The most common starting point, allowing for schedules and mood setting.
- Smart Plugs: These transform “dumb” appliances (like coffee makers or lamps) into smart ones.
- Smart Thermostats: These learn your habits to improve comfort and energy efficiency.
Step 3: Implement Intelligent Security
A “dream” home must be a fortress.
- Video Doorbells: Allow you to see and speak to visitors from anywhere.
- Smart Locks: Go keyless and track who enters or leaves your home.
- Motion Sensors: Trigger lights and send instant notifications when unexpected movement is detected.
Advanced Logic: Beyond Simple “If-This-Then-That”

The biggest gap in current DIY guides is the reliance on simple “If-Then” triggers. Real life is more complex.
AI-Powered Suggestions and Tasks
Advanced systems now use AI to help create automations. Instead of a blank slate, you can use AI to suggest names, categories, and logic for your routines. Imagine.bo takes this further with AI Tasks, allowing the system to generate data and analyze media.
Practical Implementation: The “Chicken Coop” Scenario Imagine you have a camera in a backyard coop. A traditional system can only tell you if there is motion. An AI-powered system built on a platform like Imagine.bo can use visual data to provide real insights. You can configure the system to build a computer vision app logic that:
- Takes a snapshot every 5 minutes.
- Uses image recognition to count the number of birds.
- Outputs that data into a JSON schema for your dashboard.
- Notifies you only if a bird is missing or if a predator (like a fox) is detected.
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
To achieve true scalability, your assistant needs to integrate with everything. MCP is a thin layer that allows LLMs to access to-do lists, news, or even your vinyl collection database. This makes the conversation richer: “What albums do I have by The Replacements that aren’t on my wishlist?”
Security and Privacy: The Local AI Advantage

One of the most significant outdated assumptions in smart home guides is that you must use the cloud. Cloud-based assistants come with inherent risks:
- Privacy Risks: Your private conversations and behavioral patterns are transmitted to infrastructure you don’t control.
- Latency: Sending data to a server and back introduces delays.
- Dependency: If your internet goes out, your “smart” home becomes “dumb”.
The Shift to Local AI
Forward-looking developers are moving toward Local AI, where all processing happens on edge devices. This ensures data remains on-device and private by default.
- Hardware for Local AI: Devices like Raspberry Pi 5, Jetson Nano, or Apple Silicon Macs are now capable of running lightweight LLMs (like Mistral 7B or Llama 3) locally.
- Imagine.bo Implementation: The platform is designed for end-to-end product ownership. Unlike consumer ecosystems that can change their policies or “brick” your devices overnight, Imagine.bo allows you to build a secure, high-performance assistant that operates completely without the cloud if desired.
Real-World Use Cases for the Modern Home
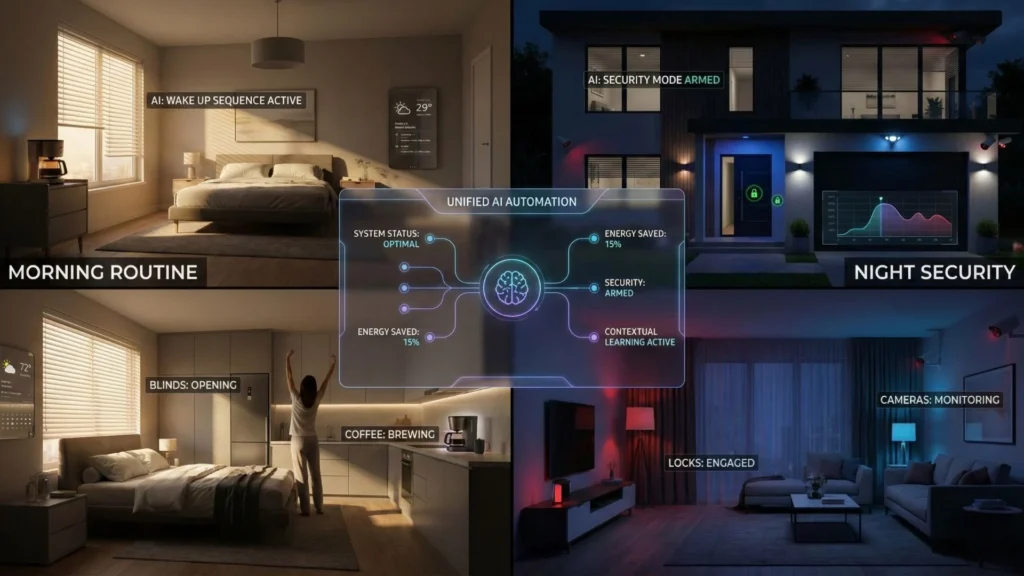
To truly understand how to build your dream smart home, we must look at integrated workflows.
Scenario A: The Proactive Morning Ritual
- 7:00 AM: The smart thermostat raises the temperature.
- 7:05 AM: The smart plug starts the coffee maker.
- 7:10 AM: Your voice assistant (configured with Imagine.bo’s AI reasoning) greets you. It doesn’t just read the weather; it analyzes your calendar, notices a heavy traffic report for your usual route, and suggests leaving 10 minutes early.
Scenario B: The Security Fortress
- 11:00 PM: You say, “Goodnight.”
- Action: The system locks all smart locks, arms the motion sensors, dims the lights, and sets the cameras to “Alert Mode”.
- AI Logic: If a motion sensor is triggered at 2:00 AM, the system doesn’t just bark an alarm. It turns on the outdoor floodlights, starts recording, and the voice assistant announces through the outdoor speaker: “You are being recorded; the authorities have been notified.”
Scalability and Future-Ready Integration

Most smart home projects fail because they don’t plan for expansion. A “dream home” should be built room by room to keep it manageable.
Why Imagine.bo for Scalability?
Typical DIY projects (like those in Python) become unmanageable as you add more devices. Imagine.bo uses an SDE-level architecture that treats every device as a modular component. This means you can:
- Start with a single smart bulb.
- Expand to a full-home security system.
- Eventually build AI-powered no-code dashboards to monitor energy consumption across every appliance.
- Zero-Coding Required: You never have to worry about “breaking the code” when you add a new device.
Conclusion
Building your dream smart home is no longer about choosing between a basic plug-and-play speaker or a complex programming project. It is about empowerment.
By following this no-code voice assistant DIY guide, you can move beyond simple gadgets and create a home that truly understands you. Whether you prioritize the privacy of Local AI, the advanced logic of AI Tasks, or the pure convenience of a voice-controlled lifestyle, the tools are now available to make it happen.
Imagine.bo stands as the ultimate platform for this journey, offering the reasoning power of an AI engineer with the simplicity of a no-code interface. It provides the scalability, security, and professional architecture needed to ensure your smart home remains a “dream” for years to come.
FAQ: Building Your Smart Home
Q: Which voice assistant is best for a beginner? A: Amazon Alexa and Google Home are excellent for those starting with basic devices due to their ease of setup and wide compatibility. For those wanting more advanced, custom logic without coding, platforms like Imagine.bo are the next logical step.
Q: Is home automation secure? A: It can be, provided you follow best practices: use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and keep your firmware updated. For maximum security, look into Local AI options where data never leaves your home.
Q: Can I use multiple voice assistants? A: Yes. Many users use Alexa for device compatibility and Google Assistant for its superior natural language processing. A central hub can help coordinate actions between them to avoid conflicts.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





