The early days of the generative AI boom were defined by a simple pattern: a user inputs text, and a single Large Language Model (LLM) outputs a response. While this approach served basic chatbots and content generators well, the architecture of successful AI products is shifting significantly as the ecosystem matures.
We are moving away from single-model dependency toward composite AI systems. These are applications that orchestrate multiple AI services – text generation, computer vision, speech synthesis, and predictive analytics – into a unified workflow.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildFor founders and builders, the challenge is no longer just accessing these models, but integrating them effectively. This is where the intersection of composite AI and no-code development becomes critical. By decoupling complex backend logic from syntax management, builders can construct sophisticated, multi-agent systems without hiring a full DevOps team.
Understanding the Power of Multi-AI Integration
To understand why combining services is necessary, we must first acknowledge the limitations of generalist models. While a model like GPT-4 is exceptionally capable, it is not optimized for every task. It can process text, but specialized models might handle image recognition, specific data extraction, or audio processing with greater accuracy or lower latency.
For example, consider an automated insurance claim app. A single-model approach would simply ask an LLM to read a text description. A multi-AI approach operates with much higher fidelity:
- Computer Vision API: Analyzes uploaded photos of vehicle damage to estimate repair costs.
- OCR Service: Extracts structured text from a police report PDF.
- LLM: Synthesizes the visual data and text data to draft a claim summary.
- Predictive Model: Compares the claim against historical fraud data.
This “chaining” logic creates a compound effect. The output of one model becomes the high-quality context for the next, significantly reducing hallucinations and increasing utility. Real-world value comes not from the AI itself, but from the orchestration of data between these intelligent nodes. If you are looking to start building, checking a comprehensive AI app development guide is a crucial first step.
Why No-Code Is the Perfect Environment for Multi-AI Apps
Historically, integrating multiple APIs required significant backend engineering. Developers had to manage authentication, handle API rate limits, normalize data formats (e.g., converting JSON to text), and manage asynchronous processes.
If a founder wanted to test the insurance app described above, they would need to write Python or Node.js scripts to glue these services together. If the image recognition API changed its response structure, the code broke. This maintenance burden often killed innovation before it started.
No-code platforms reduce this friction by abstracting the “glue code.”
Visualizing Logic Flow
In a no-code environment, the chain of AI services is represented visually. You can see the data flow from the OCR scanner into the LLM. This visual nature makes it easier to debug complex logic. If the process fails, you can visually pinpoint which node returned an error rather than parsing server logs.
Faster Iteration Cycles
When you combine multiple AI services, you are experimenting with a recipe. You might find that one image generation model is too slow, so you swap it for a faster one. In traditional coding, this requires rewriting libraries. In a sophisticated no-code setup, this is often a configuration change. This speed allows founders to focus on validating their MVP rather than API maintenance.
Core Benefits of Combining Multiple AI Services
Moving beyond a single model unlocks several architectural advantages that translate directly to business value.
Improved Accuracy and Reliability
Generalist LLMs can hallucinate when forced to perform tasks outside their primary training. Offloading specific tasks to specialized models increases overall system reliability. For instance, using a specialized math API or a code interpreter to handle calculations is far more accurate than asking a language model to do arithmetic. The LLM acts as the interface, while the specialized service acts as the engine.
Better User Experience (Multimodality)
Users interact with the world through sight, sound, and speech, not just text. A multi-AI no-code app can meet the user where they are.
- Input: A user speaks a command (Whisper API).
- Process: The system analyzes the intent (LLM).
- Output: The system generates a personalized chart (Data Visualization API) and explains it verbally (Text-to-Speech API).
This seamless transition between modalities creates a polished, professional feel that text-only AI chatbots lack.
Cost Optimization through Modular AI
Using the most powerful model (like GPT-4 or Claude 3 Opus) for every interaction is financially inefficient. A multi-AI architecture allows for “model routing.” You can use a smaller, cheaper, and faster model for basic intent classification. Only when complex reasoning is required does the system call the expensive “smart” model. This logic can reduce API costs by 40-60% at scale, which is essential for scalable SaaS architecture.
Scalability and Flexibility
If your application relies entirely on one provider, you are vulnerable to outages or price hikes. A modular approach allows you to diversify. You might use OpenAI for reasoning, Google Gemini for large context processing, and Stability AI for images. If one service goes down, you can route traffic to a backup, ensuring business continuity.
Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
The theory of multi-AI orchestration is best understood through practical application. Here is how distinct industries are utilizing this approach.
Customer Support
Modern support goes beyond simple chatbots.
- Sentiment Analysis: An initial model scans the incoming ticket to detect anger or urgency.
- Routing: Based on sentiment, the ticket is routed to the correct department.
- Drafting: An LLM drafts a response based on the company’s knowledge base.
- Translation: A translation API converts the response to the user’s native language before sending. This approach allows for true customer service automation rather than just deflection.
Healthcare
Patient intake and triage benefit heavily from chained services.
- Voice-to-Text: Captures the patient’s verbal description of symptoms.
- Entity Extraction: Pulls out key medical terms, dates, and medication names.
- Summarization: Creates a concise note for the doctor’s review.
- Compliance: A separate privacy layer creates a redacted version of the data for analytics, ensuring PII is protected. Tools for healthcare patient apps are increasingly adopting this multi-agent structure.
Finance
Financial apps require precision that LLMs alone cannot provide.
- OCR: Scans invoices and receipts.
- Validation: Cross-references extracted numbers against a database of purchase orders.
- Fraud Detection: An anomaly detection algorithm flags suspicious spending patterns.
- Notification: An LLM generates a polite, context-aware email asking for verification. This is revolutionizing how we build AI-powered financial assistants.
Retail
E-commerce is moving toward hyper-personalization.
- Visual Search: Analyzes a photo uploaded by a user to find similar products.
- Recommendation Engine: Suggests complementary items based on purchase history.
- Copy Generation: Writes unique product descriptions for thousands of SKUs automatically, optimized for SEO. Platforms serving as an AI website builder for e-commerce are natively integrating these features.
SaaS and Internal Tools
Internal dashboards are prime candidates for AI integration.
- SQL Generation: Allows non-technical managers to query databases using natural language.
- Data Visualization: Automatically converts query results into graphs.
- Report Generation: Compiles weekly metrics into a narrative PDF report distributed to stakeholders. This allows teams to automate internal tools without waiting on engineering resources.
Common Mistakes Founders Make With AI Integrations
While the potential is vast, implementations often fail due to architectural oversights.
Over-Engineering
There is a temptation to use AI for everything. Not every button click requires an LLM call. Founders often chain too many services together, resulting in a slow, expensive application. If a simple “if/then” logic statement suffices, do not use AI. Efficiency should always be the priority.
Choosing Tools Without Clear Purpose
Integrating a service just because it is popular is a recipe for technical debt. Every AI integration adds latency. If a video generation feature does not directly serve the core user problem, it is merely a distraction that slows down the app. Understanding the common mistakes in no-code SaaS development is vital to avoiding this trap.
Ignoring Data Flow and Performance
In a multi-AI chain, the output of Step A is the input of Step B. If Step A returns data in a format Step B cannot understand, the app breaks. Many builders underestimate the need for robust data transformation and error handling between these steps.
Treating AI as Magic Instead of Systems
AI is probabilistic, meaning it is not 100% deterministic. It can fail. Founders often forget to build “fallbacks.” What happens if the image generator fails? The app should fail gracefully, perhaps by showing a placeholder, rather than crashing the user’s session.
How to Choose the Right AI Services for Your App
Selecting the right stack requires a balance of performance, cost, and ease of integration.
Matching Capabilities to Business Goals
Define the problem first.
- Creativity and Nuance: High-end LLMs (GPT-4, Claude 3) are best.
- Speed and Classification: Smaller open-source models (Llama 3, Mixtral) hosted via API are superior.
- Structured Data: Specialized APIs (Serper for search, specialized OCR APIs) are better than general LLMs.
Cost vs. Performance Tradeoffs
Calculations must be done on a per-user basis. If your app requires five distinct AI calls per user session, and you have 10,000 users, the cost scales linearly. Estimate the token usage and API fees before committing to an architecture.
Data Type Alignment
Ensure the services act well together. If you are building a video app, ensure your storage solution, processing API, and streaming delivery network are compatible. Text is easy to move; video and high-res audio require significant bandwidth and storage planning.
No-Code Platforms and AI Integration
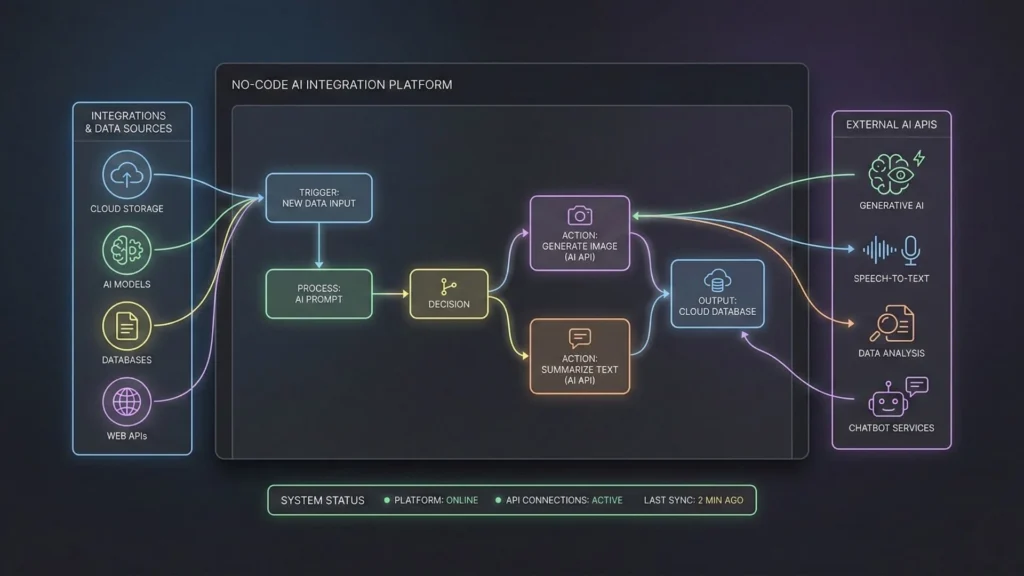
When evaluating a platform to build these systems, founders should look for specific technical traits.
API Flexibility
The platform must allow you to connect to any REST API, not just a pre-selected list. The AI landscape moves too fast to be locked into a closed ecosystem. For a deep dive, check out the top generative AI APIs for no-code developers.
Workflow Orchestration
Look for platforms that handle “logic branching.” You need the ability to say, “If the AI confidence score is below 80%, send this to a human for review; otherwise, send the email.”
Security and Scalability
Can the platform handle concurrent users? Does it manage API keys securely so they aren’t exposed in the browser? These are non-negotiable for production apps.
How Imagine.bo Supports Multi-AI No-Code Development

The platform’s architecture is designed to support the exact composite AI systems discussed in this article.
AI-Driven Planning and Architecture
Before a single line of code is generated, Imagine.bo’s system plans the database schema and API relationships. If your app requires combining Stripe for payments with OpenAI for content generation, the platform structures the data flow to ensure payment is verified before the API cost is incurred. This is the kind of logic often missed by human novices but caught by an AI architect. This is true AI-powered no-code app development.
Secure and Scalable Backend Generation
One of the risks of no-code is “spaghetti code” logic that doesn’t scale. Imagine.bo generates clean, standard code (typically Node.js/Python based architectures) running on scalable cloud infrastructure. This means your multi-AI app isn’t just a prototype; it’s built on a foundation that can handle increased traffic and multiple concurrent API requests without timing out.
Integration Handling
The platform streamlines the connection to third-party services. Whether it is a vector database for long-term memory or a specific image generation model, the system manages the secure handshake, environment variables, and data parsing, removing the most tedious parts of backend development.
Iteration Without Technical Debt
As mentioned earlier, successful apps evolve. When you need to change your AI provider or add a new service to the chain, Imagine.bo allows for rapid refactoring. You can update the requirements, and the system intelligently updates the codebase and architecture to accommodate the change without breaking existing functionality.
The Five-Step Product Workflow
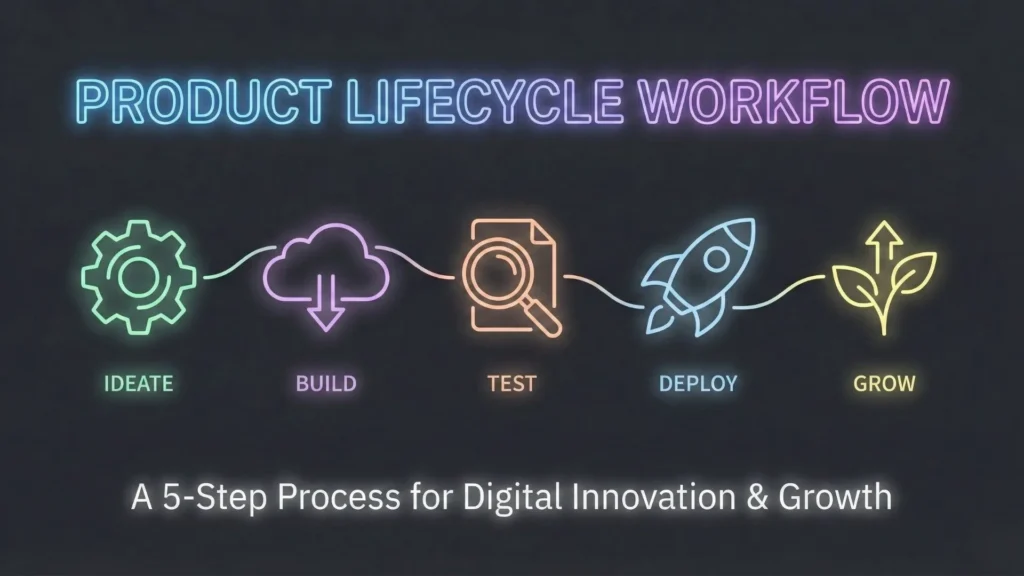
Building a sophisticated AI application requires a structured approach. Whether using traditional code or a platform like Imagine.bo, the workflow remains consistent.
1. Vision Definition
Clearly articulate the problem. “I want to solve X for Y audience.” Be specific about the inputs (data/files) and outputs (reports/media). Start by asking the right questions; see our guide on questions every founder should ask.
2. AI Reasoning and Planning
This is where the architecture is defined. Determine which AI services are needed. Map out the data journey. In Imagine.bo, this step is collaborative; the AI proposes a structure, and the user refines it.
3. Development Generation
The construction phase. This involves setting up the database, building the frontend UI, and writing the backend logic to connect the AI services.
4. Launch
Deploying the application to a live server. This includes setting up custom domains, SSL certificates, and ensuring API production keys are active. You can often launch your app without developers in a fraction of the time.
5. Ongoing Support and Evolution
Monitoring usage, fixing bugs, and updating the AI models as better versions are released. A product is never “finished,” only live.
Performance, Security, and Scalability Considerations
When you combine multiple services, you expand your “attack surface.” Security and performance must be top of mind.
Cloud-Native Deployment
Your application should reside on robust cloud infrastructure (AWS, GCP, etc.). This ensures that if your user base spikes, the servers can auto-scale to handle the load. Running heavy AI processes requires distinct server resources to prevent UI lag.
Security Standards
When handling user data – especially if sending it to third-party AIs – encryption is vital. Ensure your platform or code creates an encrypted tunnel for data in transit. Furthermore, compliance with standards like GDPR or SOC2 readiness is essential for selling into enterprise markets. You must be transparent about which AI vendors are processing user data.
Handling Growth
Scalability is about more than just servers; it’s about quotas. Ensure your accounts with AI providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) have high enough tier limits to support your expected user volume. Hitting a rate limit looks like a broken app to a user.
Who This Approach Is Best For
The composite AI approach, facilitated by next-gen no-code tools, empowers specific groups of builders.
Founders
Speed is the primary currency of a startup. This approach allows non-technical founders to validate complex ideas in weeks rather than months, preserving runway.
Domain Experts
A lawyer knows exactly how a contract should be analyzed but doesn’t know Python. A doctor knows how triage should work but can’t write code. These tools allow experts to build solutions that encode their specific knowledge into the AI workflow.
Small Teams
Startups with limited engineering resources can punch above their weight. Small teams can scale big by leveraging AI for the heavy lifting.
Product Designers
Designers who understand user flow and experience can now own the full stack. They can ensure the interaction with the AI feels natural and human, rather than robotic and clunky.
Conclusion
The era of simple AI wrappers is closing. The next generation of successful SaaS products will be defined by their ability to intelligently weave together text, image, voice, and data services into cohesive workflows.
For the builder, the barrier to entry has never been lower, but the requirement for clear architectural thinking has never been higher. Platforms that combine powerful AI reasoning with rigorous engineering standards – handling the “how” so you can focus on the “what” – will define the future of software development.
Thoughtful integration, robust security, and a focus on solving genuine user problems will always outperform hype. The tools are ready; the opportunity lies in how you choose to combine them.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





