Understanding the MVP Concept
Defining a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP isn’t about building the *least* amount of product; it’s about building the *least* amount necessary to validate your core assumptions. It’s a strategic approach, focusing on delivering core functionality to early adopters. This allows for rapid iteration based on real user feedback, minimizing wasted resources on features nobody wants. Think of Eric Ries’s popular lean startup methodology; his work emphasizes the importance of learning quickly and adapting your product based on data, not guesswork. This iterative process is crucial for MVP success.
Successfully defining your MVP requires a laser focus on your target audience and their key needs. Ask yourself: What are the absolute minimum features required to solve their problem and get their initial feedback? “Prioritize features that directly address the core value proposition and provide a compelling user experience, even if it’s a simplified one.” Remember, the goal is to learn, not to create a perfect product from the outset. Examples like Dropbox’s initial video demonstrating the product’s core functionality before full development showcase the power of this approach. A well-defined MVP is the foundation for a successful product launch.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildWhy Build an MVP: Key Benefits and Advantages
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) offers significant advantages for startups and established businesses alike. It drastically reduces the risk associated with launching a completely new product or feature. By focusing on core functionality, you can test your assumptions quickly and cheaply. This iterative approach allows for rapid feedback and adjustments, ensuring your final product better meets market demands. Think of companies like Dropbox, which initially launched as a simple video demonstrating the core value proposition before investing heavily in development. This significantly de-risked their launch and allowed them to refine their offering based on real user feedback.
The benefits extend beyond risk mitigation. An MVP helps you validate your business idea before committing significant resources. You’ll gain valuable insights into user behavior and preferences, informing future development. This data-driven approach is crucial for optimizing your product-market fit. Furthermore, a successful MVP launch can generate early adopters and build crucial momentum. “Launching an MVP allows you to acquire early users and build a community around your product, fostering valuable feedback and brand loyalty even before a fully-fledged product is available,” Ultimately, a well-executed minimum viable product development strategy can save time, money, and resources while maximizing the chances of success.
Common Misconceptions about MVPs
Many believe an MVP is a rushed, low-quality product. This is incorrect. A successful MVP prioritizes core features, delivering a functional product showcasing the core value proposition. It’s about learning, not launching a flawed final product. Think of Dropbox’s initial video demonstrating the core functionality – that was their MVP, far from a shoddy version of their current offering.
Another misconception is that an MVP needs to be visually stunning. While good design is valuable, it’s secondary to functionality in the MVP stage. Focus on solving the core problem effectively. Spending excessive time on aesthetics before testing the core concept wastes resources. Remember, the goal isn’t perfection; it’s validation. “A well-executed MVP gathers crucial user feedback, enabling iterative improvements before significant investment in design and advanced features.” This allows for a more efficient and effective product development lifecycle, saving time and money in the long run.
Choosing the Right MVP Builder Tools and Platforms

No-Code/Low-Code MVP Builders: A Review of Popular Options
No-code and low-code platforms offer a rapid route to MVP development, particularly for those lacking extensive coding skills. Popular choices include Webflow, Bubble, and Softr. Webflow excels in building visually appealing websites, ideal for showcasing a product or service. Bubble provides more flexibility for complex applications, allowing for custom backend logic. Softr, on the other hand, is specifically designed for quickly creating Airtable-based applications, streamlining the process if your data resides there. Consider your technical expertise and the complexity of your MVP when making your selection.
“The right platform depends heavily on your specific needs.” For simple MVPs with a strong visual focus, Webflow might be perfect. However, for more intricate functionalities or integrations with existing systems, Bubble or Softr might be better suited. Remember to carefully evaluate each platform’s features, pricing models, and community support before committing. Researching user reviews and tutorials can provide invaluable insights before you begin building your minimum viable product.
Code-Based MVP Development Platforms and Frameworks
For tech-savvy entrepreneurs, building an MVP from scratch using code offers maximum control and customization. Popular code-based MVP development platforms include React, Angular, and Vue.js for front-end development, alongside robust back-end frameworks like Node.js, Ruby on Rails, or Python’s Django. These frameworks provide pre-built components and functionalities, accelerating the development process. Choosing the right framework depends on your team’s expertise, project requirements, and scalability needs. For example, React’s component-based architecture excels in building dynamic user interfaces, while Node.js’s non-blocking I/O model is ideal for real-time applications.
Remember, building a code-based MVP demands technical expertise. If you lack in-house developers, consider outsourcing to experienced freelancers or agencies. Thoroughly vet potential developers and clearly define project scope, timelines, and deliverables upfront. “This proactive approach minimizes risks and ensures a successful MVP launch.” Efficient project management tools, such as Jira or Trello, can further streamline the development process and enhance communication. Carefully consider the long-term maintenance and scalability implications of your chosen framework before committing to it.
Selecting the Best MVP Builder for Your Project: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right MVP builder is crucial for your project’s success. Consider your technical skills. Are you a coder? Or do you need a no-code/low-code solution? Platforms like Bubble or Webflow cater to less technical founders, while frameworks like React or Ruby on Rails require coding expertise. Also, factor in your budget. Some platforms offer free tiers, while others charge monthly or per-project fees. “Carefully analyze the pricing models and ensure they align with your financial resources.” Finally, think about scalability. Will your chosen platform support your future growth? Choose a solution that allows for easy expansion and integration with other tools as your MVP evolves.
Your project’s specific needs should heavily influence your decision. For example, if you’re building a mobile-first app, a platform with strong mobile development capabilities is essential. Conversely, a web application might benefit from a platform specializing in backend infrastructure or specific integrations. “Don’t underestimate the importance of community support and available documentation.” A robust community can provide valuable assistance during the development process. Look for platforms with active forums, comprehensive documentation, and readily available tutorials to aid you. Finally, remember to thoroughly test any platform before committing, utilizing free trials or demos whenever possible.
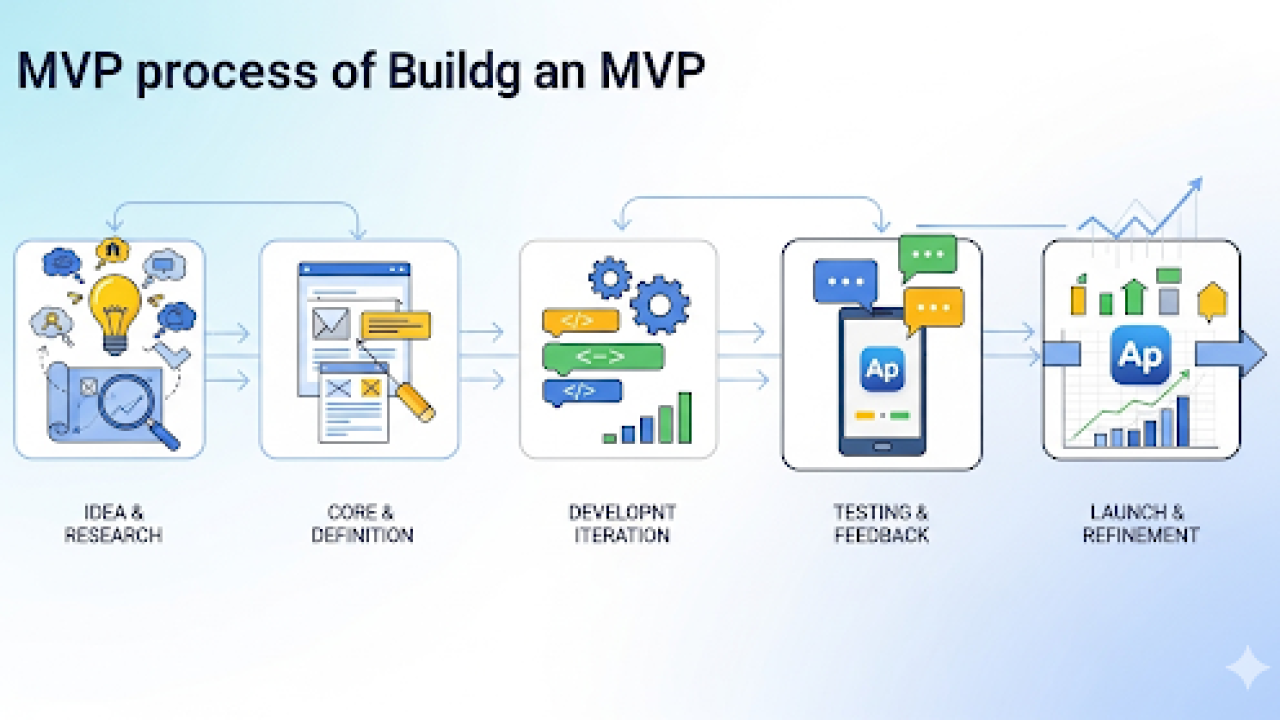
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your MVP
Defining Your MVP’s Core Features and Functionality
Defining your MVP requires ruthless prioritization. Focus on the absolute core functions that deliver essential value to your early adopters. Ask yourself: What is the single most important problem your product solves? What features are absolutely necessary to demonstrate that solution? For example, a social media app’s MVP might only include user profiles, posting, and following, foregoing advanced features like direct messaging or group chats initially. This allows for faster development and quicker user feedback.
Remember, the goal is not to build everything you *could* build, but everything you *need* to build to validate your core concept. “A successful MVP should be functional enough to attract early users and gather valuable feedback for future iterations,” leaving room for expansion based on real-world usage. This iterative approach, common in agile development methodologies like Scrum, minimizes wasted effort and maximizes learning. Consider using tools like user story mapping to visualize and prioritize features effectively. Prioritize the features that solve the core problem for your target audience first.
Prioritizing Features Based on User Needs and Business Goals
Defining your MVP’s core functionality requires a laser focus on user needs and your overarching business objectives. Start by thoroughly researching your target audience. Utilize techniques like user surveys, interviews, and competitive analyses to understand their pain points and desires. This crucial step ensures you build a product people actually want. Remember, a successful MVP isn’t about cramming in every possible feature; it’s about delivering essential value efficiently. For example, Dropbox’s initial MVP focused solely on file synchronization, ignoring extra features like file sharing until later iterations, proving its effectiveness.
Next, align those user needs with your business goals. Create a prioritized feature list using a method like the MoSCoW method (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have). This framework helps you objectively assess which features are vital for launch and which can be added later. Prioritization ensures you build a product that solves the most pressing problems while aligning with your revenue model and overall business strategy. “Failing to prioritize features can lead to scope creep, budget overruns, and a delayed launch, ultimately jeopardizing the success of your MVP.” This focused approach guarantees your efforts are directed toward the most impactful aspects of your minimum viable product.
Iterative Development: Building and Testing in Stages
Forget the idea of building a perfect product upfront. Iterative development, championed by companies like Dropbox and Airbnb in their early stages, is key to MVP success. It involves building your MVP in small, manageable stages. Each stage focuses on a core feature or functionality. This allows for continuous testing and refinement based on user feedback. You’ll release a basic version, gather data, and then improve it. This process reduces risk and maximizes the chances of building something users truly want.
After each iteration, you analyze data. This data might come from user surveys, A/B testing, or analytics tracking. Then, you prioritize features for the next iteration. You should always focus on the features that deliver the most value to your users. This agile approach ensures you’re not wasting resources on unnecessary features. “By consistently incorporating user feedback and data analysis, you’ll drastically improve your chances of building a successful minimum viable product.” Remember, an MVP is a living thing; it evolves over time, becoming more robust and refined with each iteration.
Testing and Iterating Your MVP
Gathering User Feedback: Effective Methods and Strategies
Gathering user feedback is crucial for MVP success. Effective methods include user interviews, where you directly engage with potential users to understand their needs and experiences. Consider using a structured interview guide to ensure you cover key areas, such as ease of use and overall satisfaction. A/B testing different features or design elements provides quantifiable data on user preferences. For example, Dropbox famously used A/B testing throughout their development, optimizing their interface based on user response. This data-driven approach allows for iterative improvements.
Furthermore, consider utilizing online surveys and feedback forms for broader reach. These tools offer a simple and scalable way to gather diverse opinions. Remember to keep your questions concise and focused. Analyzing this feedback helps identify areas for improvement. “Regularly soliciting and acting upon user feedback is essential for iterative development and creating a truly valuable product.” Don’t just collect data; actively analyze it to pinpoint usability issues and areas needing design refinements. Tools like Hotjar provide visual heatmaps, showing where users interact most with your MVP.
Analyzing User Data and Identifying Areas for Improvement
Once your MVP is launched, the real work begins: gathering and analyzing user data. Tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or even simple surveys provide invaluable insights. Pay close attention to user engagement metrics, such as session duration, feature usage, and conversion rates. Low engagement with a specific feature? That’s a clear signal for improvement. Remember, even seemingly insignificant data points can reveal crucial information about user behavior and preferences. For example, a high bounce rate on a particular page might suggest poor navigation or unclear messaging.
Analyzing this data allows you to pinpoint areas needing attention. Prioritize improvements based on their impact on your key performance indicators (KPIs). Perhaps a small UI adjustment dramatically increases conversion, or a clearer onboarding process reduces user churn. “Remember, iterative development is crucial for MVP success; don’t be afraid to experiment and adjust based on real user feedback.” Use A/B testing to compare different versions of features, helping you make data-driven decisions, and ultimately leading to a more refined and successful product. Continuously monitoring and adjusting based on user data ensures your MVP evolves into a product that truly meets user needs.
Iterating Based on Feedback: Refining Your MVP for Optimal Performance
Analyzing user feedback is crucial for successful MVP iteration. Look beyond simple satisfaction scores. Dive deep into qualitative data, such as user comments and interview transcripts. Identify recurring pain points or areas of confusion. This will pinpoint features needing improvement or complete removal. Prioritize changes based on their impact on user experience and overall business goals. For example, a company launching a new e-commerce platform might discover through user testing that the checkout process is overly complicated, leading to high cart abandonment. Addressing this critical issue should be a top priority.
Prioritize iterative changes rather than attempting a complete overhaul. Small, focused iterations allow for controlled testing and quicker adaptation. Use A/B testing to compare different versions of your MVP features. For instance, compare two different button designs to see which improves click-through rates. “Continuously monitoring key metrics, such as user engagement and conversion rates, will provide clear evidence of your progress and guide further refinements.” Remember, the goal is to optimize your MVP for both user satisfaction and business success through a process of continuous improvement. Document all changes and their impact, creating a valuable knowledge base for future development.
Launching and Scaling Your MVP
Preparing for MVP Launch: Marketing and Promotion Strategies
Before launching your minimum viable product (MVP), a robust marketing and promotion strategy is crucial. This isn’t about a massive, expensive campaign. Instead, focus on identifying your target audience and crafting messaging that resonates with their needs. Consider leveraging low-cost, high-impact strategies like social media marketing, targeted online advertising (perhaps using Google Ads), and content marketing, such as blog posts showcasing your MVP’s unique value proposition. Early adopters are key; engage with them directly through email newsletters and online communities. For example, Buffer, a popular social media management tool, successfully utilized early adopter feedback to iteratively improve their MVP.
Successful MVP launch requires more than just a great product; it needs a plan to get it in front of the right people. “Pre-launch buzz generation is vital,” creating anticipation and building a community around your product. This could involve teaser campaigns on social media or offering exclusive early access to a select group of users. Gather email addresses through landing pages offering valuable content related to your MVP’s functionality. Post-launch, meticulously track key metrics like website traffic, user engagement, and conversion rates to inform your next steps. Analyze this data to understand what’s working and what needs adjustment in your MVP scaling strategy.
Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Post-Launch
Post-launch monitoring is crucial for your MVP’s success. You need to track key performance indicators (KPIs) diligently to understand user behavior and identify areas for improvement. Common KPIs include user acquisition cost, customer lifetime value (CLTV), daily/monthly active users (DAU/MAU), conversion rates, and customer churn rate. Regularly reviewing these metrics provides vital insights into your product’s performance and market fit. For example, a high churn rate might signal a usability problem needing immediate attention. Analyzing data allows for data-driven decisions to optimize the user experience.
Effective KPI monitoring involves using analytics tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Amplitude. These tools provide comprehensive data visualization and reporting features. Set realistic targets for your KPIs based on industry benchmarks and your specific goals. Regularly analyze your data, ideally weekly or bi-weekly, to identify trends and potential issues promptly. “Don’t wait for problems to become crises; proactive monitoring is key to a successful MVP launch and scaling strategy.” Remember, adapting your MVP based on user feedback and data analysis is an iterative process. This ensures your product continuously improves and better meets your target market’s needs.
Scaling Your MVP: From Minimum to Sustainable Product
Scaling your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) requires a strategic approach. You’ve proven core functionality; now, focus on user feedback. Analyze user data rigorously. Identify features driving engagement and those causing friction. Prioritize improvements based on this data, focusing on areas offering the greatest return on investment. Tools like Mixpanel and Amplitude can provide invaluable insights into user behavior. Remember, iterative development is key. Release updates frequently, incorporating user feedback and addressing bugs swiftly. This agile approach keeps your product relevant and improves user retention.
Successful scaling isn’t just about adding features. It’s about building a sustainable product. This means focusing on infrastructure, scalability, and long-term maintainability. Consider cloud infrastructure solutions like AWS or Google Cloud to handle increased traffic and data storage. Invest in robust testing and quality assurance procedures to minimize bugs and ensure stability as your user base grows. “Continuously monitoring your key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for measuring success and guiding future development.” This data-driven approach ensures your MVP evolves into a robust, sustainable product that meets evolving market demands and user expectations.
Real-World MVP Examples and Case Studies
Analyzing Successful MVP Launches and Their Strategies
Examining successful MVP launches reveals common threads. Dropbox, for instance, used a simple video demonstrating its core functionality—file syncing and sharing—before even writing a single line of code. This clever strategy validated their concept and garnered significant early interest, proving the market demand for their minimum viable product. They prioritized showcasing the problem they solved and the ease of their solution, effectively bypassing extensive upfront development. This approach, focusing on core features and user feedback loops, is critical for effective MVP development.
Furthermore, Airbnb’s initial launch focused on a limited number of listings in a specific geographic area. This allowed them to test their platform’s functionality and gather essential user feedback. They iteratively improved their platform based on real-world usage, adding features only after confirming user demand. “This data-driven approach allowed Airbnb to fine-tune their offering and avoid costly mistakes often associated with premature feature additions.” Their success highlights the importance of launching early, gathering feedback and iterating rapidly—crucial elements of a successful MVP development lifecycle.
Learning from MVP Failures: Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Many promising MVPs fail due to neglecting crucial aspects of product development. For example, the initial version of Google’s search engine, BackRub, was hampered by its inability to scale effectively. This highlights the importance of prioritizing scalability from the outset. Ignoring user feedback is another common mistake. Consider Color, a photo-sharing app that failed despite significant initial investment. They didn’t adequately adapt to user needs and preferences, leading to their downfall. These failures underscore the need for robust testing and iterative development.
To avoid similar pitfalls, thoroughly research your target market and validate your assumptions before committing significant resources. “Focus on solving a specific problem effectively, rather than building an overly ambitious product with too many features.” A lean approach is key: Prioritize essential features, gather user data, and iterate based on feedback. Remember, your MVP is not a finished product, but a learning tool. Continuously evaluate and adapt your MVP to minimize the risk of costly failures and maximize its chances of success. This iterative process is crucial for transforming a viable concept into a successful product.
Case Studies of MVPs Across Various Industries
Dropbox, a file hosting service, launched with a simple video demonstrating its functionality. This minimum viable product (MVP) cleverly bypassed the need for extensive initial development by focusing on the core value proposition: easy file sharing. This streamlined approach allowed them to quickly gather user feedback and iterate based on real-world usage, ultimately leading to their massive success. Their lean approach to launching an MVP showcases the power of prioritizing core features and testing assumptions early.
In contrast, consider the social media giant, Twitter. Their initial launch featured a remarkably limited feature set – far less than the platform we know today. This initial MVP centered around short, text-based messages, allowing them to quickly test the market’s appetite for micro-blogging. The rapid iteration and development based on user feedback—from character limits to direct messaging—ultimately helped shape the Twitter we use today. “This highlights how focusing on a core, solvable problem with a simple MVP can lead to rapid growth and adaptation.” Both examples powerfully illustrate the effectiveness of a well-planned MVP strategy across vastly different industries.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build