Shift your focus from manual syntax to Vibe Coding, a modern development paradigm where natural language drives Build AI Agents with Vibe Coding. Instead of fighting boilerplate, you act as the architect, using intention to guide AI through reasoning loops and orchestration.
Whether using platforms like Imagine.bo for no-code scalability or standard IDEs, this guide reveals how to structure specs and enforce security rules. Master this workflow to cut development costs by 70% and prioritize solving actual problems over writing lines of code.
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
BuildUnderstanding Vibe Coding: Intention Over Syntax
Vibe coding is not a “crutch” for those who cannot program; it is an amplifier for those who solve problems. In this paradigm, English is the hottest new programming language.
Why It Matters
- Contextual Intelligence: Modern tools understand not just what you are building, but how you prefer to build it.
- Elimination of “Infrastructure Friction”: Traditionally, developers spent 80% of their time on setup (CORS, database connections, job schedulers). Vibe coding allows you to bypass this “creative death” by using unified interfaces.
- The Director Metaphor: Think of yourself as a movie director. You aren’t holding the camera or setting the lights; you are telling the crew, “Make this scene feel tense and consistent”. The AI agent is your production crew.
Architecting AI Agents: Reasoning, Orchestration, and Scaling

Building an AI agent is fundamentally different from building a traditional app. An agent is a self-directed program that makes decisions independently to achieve a goal.
The Reasoning Loop
Modern agents use reasoning engines to bridge the gap between a prompt and production code.
- Step-by-Step Logic: Advanced agents do not build everything at once. They generate a phased implementation plan, review the code for flaws, and iterate until the functionality is proven.
- Function Calling: Agents use tools (APIs, databases) via “tool calling” to interact with the real world.
- Context Management: Effective agents require clean context. When a conversation becomes too “heavy” (exceeding context windows), the agent’s reasoning degrades, requiring a session reset with a fresh specification.
Orchestration and Tooling
To move beyond simple chat, agents utilize the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This allows an AI assistant to connect directly to external data sources, databases, and local documentation. For high-level builds, platforms like Imagine.bo integrate these reasoning engines with SDE-level architecture, ensuring that the generated code isn’t just a prototype, but a scalable SaaS architecture.
Traditional vs. AI-First Development: A Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Development | AI-First (Vibe Coding) |
| Logic Entry | Manual syntax (JS/Python) | Natural language intent |
| Backend | Manual AWS/Postgres/CORS setup | Unified abstractions (e.g., app.crudlify()) |
| Iteration | Manual refactoring and debugging | Conversational debugging and AI-led PRs |
| Focus | How it works (Implementation) | What it does (Architecture/Design) |
Example: In a traditional setup, creating a secure CRUD API might take hours of boilerplate. In an AI-first development workflow, you simply describe the database schema, and the agent scaffolds the API, authentication, and rate limiting in seconds.
A Practical Workflow for Modern Builders
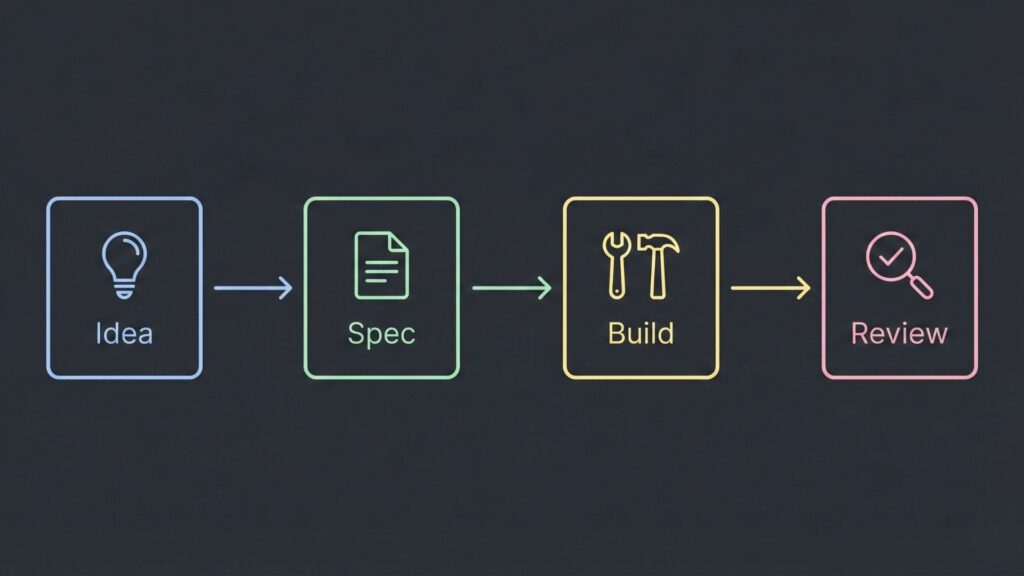
To build a production-grade agent, follow this “Structured Vibe Coding” approach:
- Define the Spec: Write a detailed Project Requirements Document (PRD) including data schemas, user flows, and specific tech stacks.
- Generate a Task Backlog: Ask the agent to break the spec into a
todo.mdfile. - Phase Implementation: Implement one feature at a time. Review the agent’s code as an “Editor-in-Chief”.
- Enforce Rules: Use project-specific rules (e.g.,
.cursor/rulesor.mdcfiles) to force the AI to stick to your architecture and avoid “logic drift”.
For a deeper dive into this process, check out our guide on how to vibe code apps with AI.
Scaling, Security, and Production Readiness
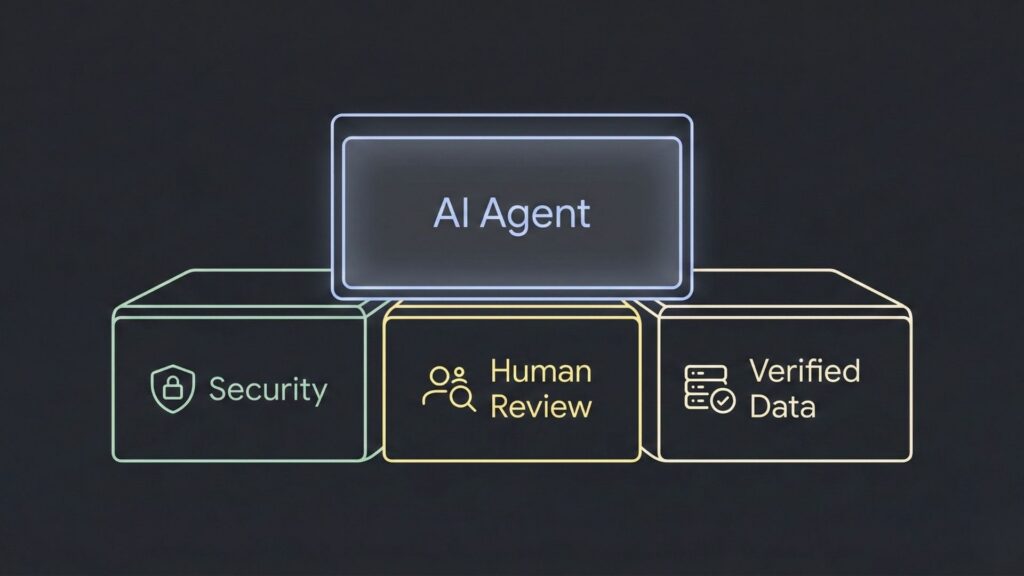
The “GenAI Divide” occurs when a flashy pilot fails to become a secure, scaled application.
Production Standards
- Human-in-the-Loop: Never trust AI output blindly. You must review pull requests (PRs) and run automated tests before merging.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Give agents the bare minimum access they need to prevent accidental data overreach.
- Grounded RAG: To stop hallucinations, use Agentic RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). This ensures the agent’s decisions are grounded in your verified business data.
Positioning Imagine.bo for Scale

Please note: Information regarding Imagine.bo is not from the provided sources and should be independently verified.
While tools like Cursor or Windsurf are excellent for IDE-based development, Imagine.bo provides an end-to-end, no-code platform specifically for founders. It combines a reasoning engine with SDE-level architecture, allowing non-technical builders to collaborate with AI to create revenue-ready apps. It addresses the “backend complexity” that typically kills the vibe by handling cloud deployment and security standards automatically.
Takeaways for Builders
- Plan before you prompt: High-quality documentation leads to high-quality code.
- Commit often: Frequent Git commits allow you to roll back when an agent “hallucinates” a major architectural change.
- Bridge the gap: Use platforms that offer both low-code simplicity for business logic and full API access for technical scaling.
Conclusion: The Future is Powered by Vibe
We are entering an era where anyone with a clear goal can participate in software development. By treating AI agents as teammates rather than just autocomplete tools, you can reduce development costs by up to 70% and ship 10x faster.
The goal isn’t to write code—it’s to solve problems. Whether you are a solo founder using a no-code engine like Imagine.bo or a senior engineer architecting complex multi-agent systems, the “vibe” is your new competitive advantage.
Analogy: Building an agent today is like using a GPS. You no longer need to know how to read a paper map or understand the internal combustion engine (syntax/infrastructure); you just need to know exactly where you want to go (intent) and stay alert to ensure the “driver” doesn’t take a wrong turn (review).
Launch Your App Today
Ready to launch? Skip the tech stress. Describe, Build, Launch in three simple steps.
Build





